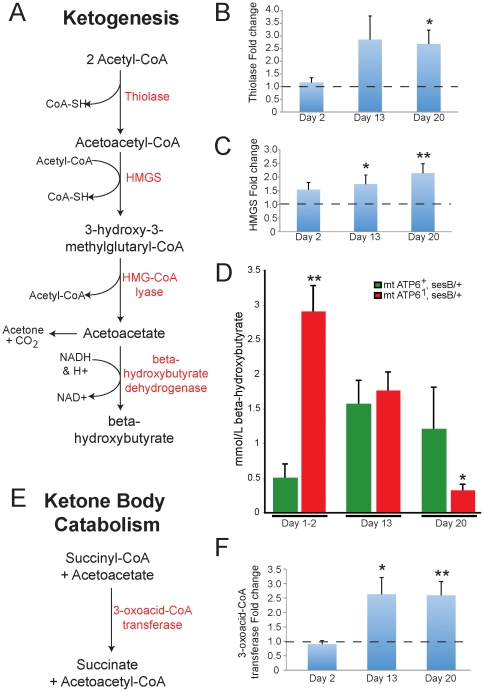
Figure 4. Ketogenic compensation in ATP61 animals.
A) The ketogenic metabolic pathway is used to produce ketone bodies (acetoacetate, acetone and beta-hydroxybutyrate). Enzymes shown in red. B & C) Real-time quantitative RT-PCR of the enzyme thiolase and 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA synthase (HMGS) reveal an increasing trend in ATP61 animals with age compared to wildtype. N = 12 wildtype each time point. N = 12 ATP61 each time point. Error is S.E.M. Statistical analysis is student's t-test. D) Quantitation of beta-hydroxybutyrate shows a marked increase in young animals with a decreasing trend with age compared with wildype. N = 9 wildtype day1–2, N = 5 wildtype days 13 and 20. N = 6 ATP61 day 1–2, N = 5 ATP61 days 13 and 20. Error is S.E.M. Statistical analysis is student's t-test. E) The enzyme 3-oxoacid-CoA transferase is involved in ketone body catabolism. F) Real-time quantitative RT-PCR of 3-oxoacid-CoA transferase reveals an increasing trend with age in ATP61 animals versus controls. N = 12 wildtype each time point. N = 12 ATP61 each time point. Error is S.E.M. Statistical analysis is student's t-test.