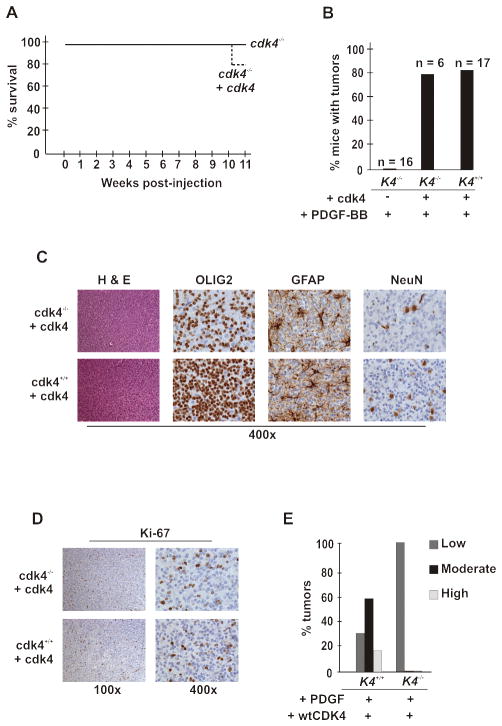
Figure 3. Expression of cdk4 in cdk4 knockout glial cells restores development of glial tumors, but not progression.
(A) Reconstitution of nestin-positive progenitors in cdk4 knockout mice with cdk4 does not change survival from knockout levels following challenge with PDGF. Six neonatal cdk4 knockout nestin-tvA mice were injected intracranially with DF-1 chicken cells expressing RCAS-HA-PDGF and RCAS-cdk4, either singly or in combination. Mice were subsequently followed and assessed as described in the legend to Figure 1A. (B) Gross tumor formation was determined by H & E staining as described in the legend to Figure 1B. (C) Tumors in reconstituted cdk4 knockout mice were classified oligodendroglioma by immunostaing for OLIG2, GFAP and NeuN. Brown deposits represent positive staining. (D) Ki-67 staining. Positive proliferating cells marked by Ki67 stain are brown. (E) Tumor cell reconstitution of cdk4 does not correct the progression defect in glioma. Tumors from the wild type mice and cdk4 knockout mice in which cdk4 expression was reconstituted in oligodendrocytes were graded and plotted as described in the legend to figure 1C.