Figure 5. The absence of cyclin D1 does not affect the infiltration of stromal-derived cells into glial tumors, but alters the activation state of tumor-associated microglia.
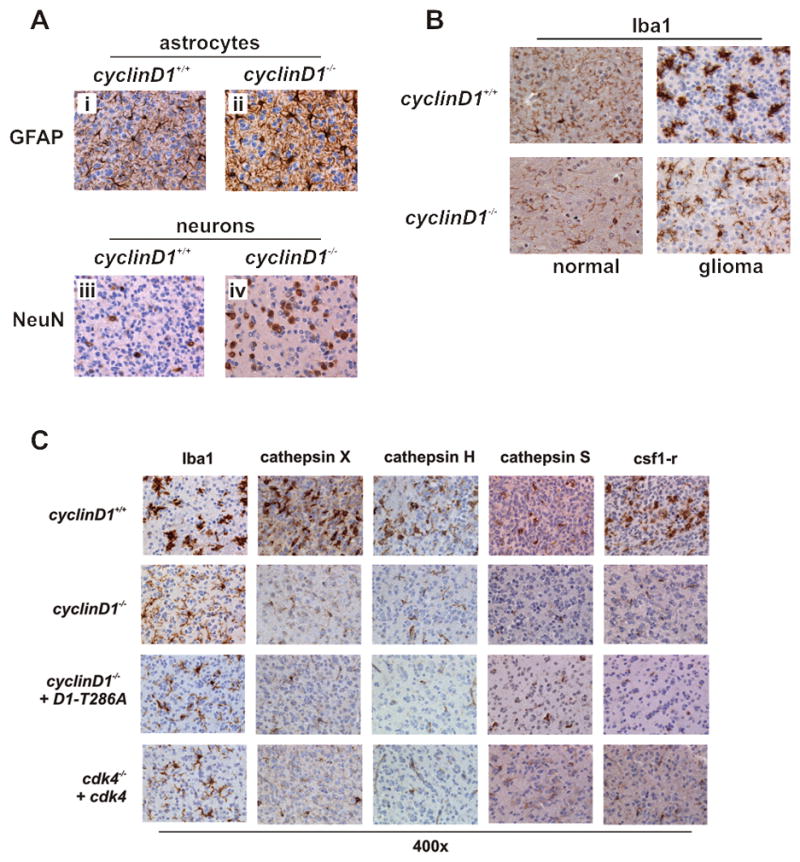
(A) Tumors from wild type and cyclin D1 knockout animals symptomatic for glioma were fixed in formalin and stained with antibodies to GFAP (reactive astrocytes; i and ii) and NeuN (neurons; iii and iv). (B) TAMs, marked by Iba1 staining. (C) Gliomas arising in the cyclin D1 knockout mice and cyclinD1 and cdk4 knockout mice in which the cyclinD1-cdk4 axis has been reconstituted in the tumor cell-of-origin were assessed for microglia activation by Iba1, cathepsin X, H and S and CSF1R immunohistochemistry. Activation status of TAMs TAMs in cyclinD1 knockout gliomas express and secrete reduced levels of cathepsin X.
