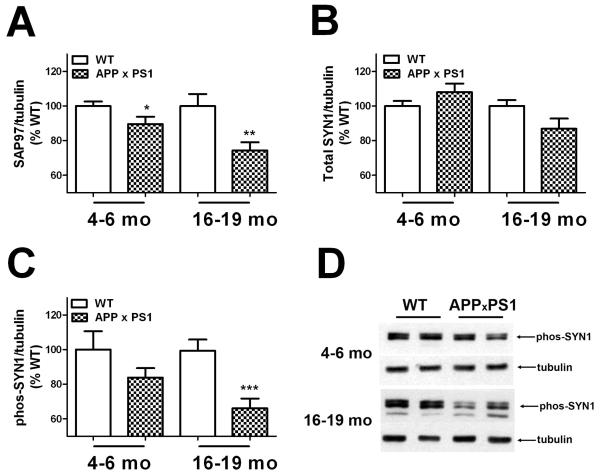
Figure 2. Age-related decreases in synaptic marker expression in APP × PS1 mice.
(A) Expression of the post-synaptic protein synapse associated protein 97 (SAP97) was evaluated in tissue homogenates prepared from the frontal cortex of young (4-6 month–old) and aged (16-19 month–old) APP × PS1 and WT mice by Western blot as described in Methods. For consistent quantification across multiple blots, individual samples were normalized first to tubulin and then to levels in WT mice, as described in Methods. Data are mean ± SEM SAP97 expression in 19-20 mice/group, and were analyzed by 2-tailed, unpaired t-tests. * and ** indicate significant (p < 0.05 and 0.01, respectively) decreases in SAP97 expression detected in young and aged APP × PS1 mice, respectively. (B) Expression of the pre-synaptic protein synapsin 1 (SYN1) was evaluated in tissue homogenates prepared from the frontal cortex of young (4-6 month–old) and aged (16-19 month–old) APP × PS1 and WT mice as described in Methods. Data are mean ± SEM SYN1 expression in 19-20 mice/group. (C) Expression of phosphorylated synapsin 1 (phos-SYN1) was evaluated in tissue homogenates prepared from the frontal cortex of young (4-6 month–old) and aged (16-19 month–old) APP × PS1 and WT mice as described in Methods. Data are mean ± SEM phos-SYN1 expression in 19-20 mice/group, and were analyzed by 2-tailed, unpaired t-tests. *** indicates significant (p < 0.001) decreases in phos-SYN1 expression in aged APP × PS1 mice as compared to aged WT mice. (D) Representative images depict the pattern of phos-SYN1 expression in young and aged APP × PS1 and WT mice.