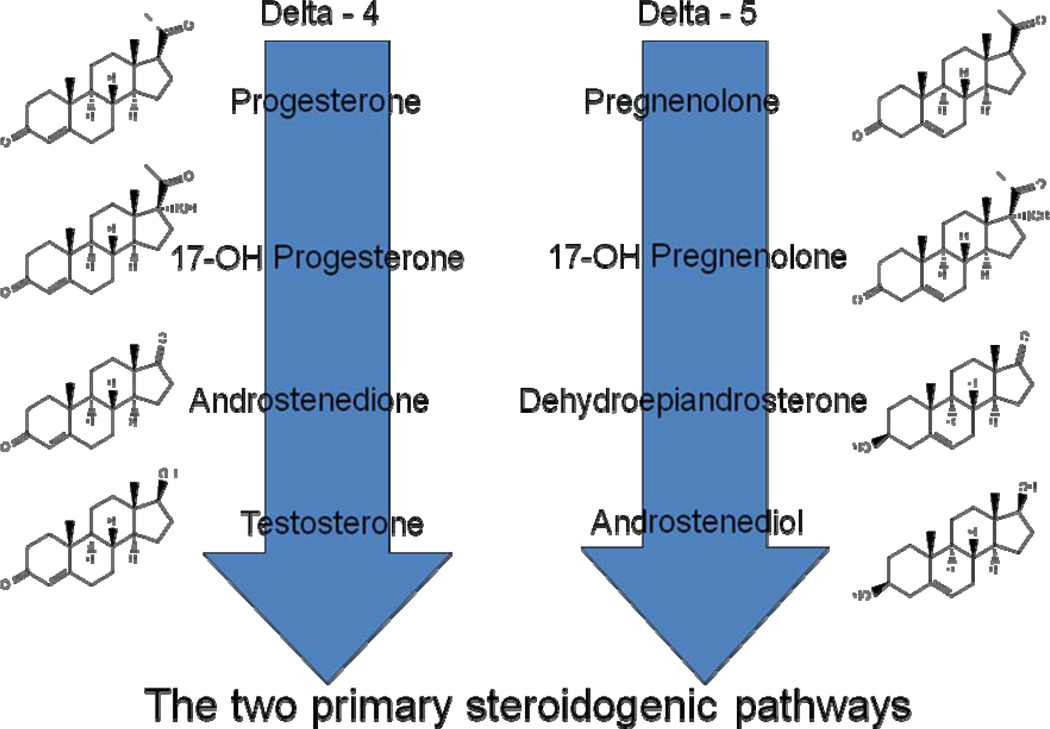
Figure 3.
The two primary adrenal steroidogenic pathways. The delta four pathway on the left has been considered to be the critical pathway giving rise to the mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids as well as androstenedione and testosterone which can be aromatized peripherally to estrogen and estradiol, respectively. The delta five pathway on the right has been considered important mainly for the production of dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate which can be prohormones for peripheral conversion to more bioactive steroids. The steroidogenic enzyme, 3-betahydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (or delta 4/5 isomerase) converts delta-5 to delta-4 hormones. Androstenediol, because it is now recognized to circulate in relatively high concentrations, is now be considered to be important during the menopausal transition.