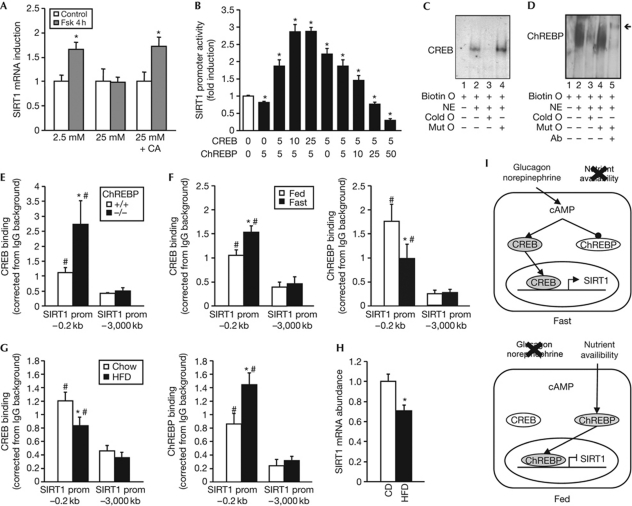
Figure 4.
The regulation of SIRT1 by CREB and ChREBP is interdependent and coordinated by energy availability. (A) HepG2 cells were stimulated for 4 h with 10 μM forskolin in 2.5 mM or 25 mM glucose. A third group was treated with CA 1 h before treatment of forskolin in 25 mM glucose. SIRT1 mRNA levels were then measured by qPCR. Data are relative to the control group. (B) HepG2 cells were transfected with the SIRT1 promoter luciferase reporter and with the indicated amount (ng) of pCMV–CREB and ChREBP/Mlx. Luciferase activity was measured as described (n=6). (C) EMSA was performed using nuclear extracts from CHO cells transfected with CREB and a 25-bp biotinylated oligonucleotide with the overlapping core sequence for CREB and ChREBP. (D) EMSA was performed as in C, using nuclear extracts from CHO cells transfected with Flag-tagged ChREBP and its partner Mlx. Arrow indicates the supershifted band. (E) ChIP was performed in the liver from fed ChREBP+/+ or ChREBP−/− mice using an IgG control or CREB-specific antibody. (F) ChIP was performed in the liver from fed or 18 h-fasted mice using an IgG control, CREB- or ChREBP-specific antibody. (G) ChIP was performed in the liver from mice fed chow or HFD using an IgG control or CREB- or ChREBP-specific antibody as described previously. (H) SIRT1 mRNA abundance in the liver of mice fed chow or HFD. Values are presented as the average±s.e.m., asterisk indicates a statistical difference compared with control/empty vector/ChREBP+/+/FED or chow, and hash symbol indicates statistical difference compared with distal promoter at P<0.05. (I) Scheme illustrating how nutrient availability is integrated by CREB and ChREBP to coordinately regulate SIRT1 expression. During fasting, glucagon and norepinephrine lead to an increase in cAMP and PKA activity, in turn leading to CREB activation and ChREBP inactivation. CREB then induces SIRT1 expression. Conversely, during the fed state, ChREBP binds to the SIRT1 promoter to downregulate its expression, potentially through competition with CREB binding (bottom panel). Ab, flag-specific antibody; biotin O, biotinylated oligonucleotide; CA, cantharidic acid; cAMP, cyclic AMP; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; ChREBP, carbohydrate response-element-binding protein; cold O, cold oligonucleotide excess; CREB, cAMP response-element-binding protein; EMSA, electrophoretic mobility shift assay; Fsk, forskolin; HFD, high-fat diet; IgG, immunoglobulin G; mut O, cold mutant oligonucleotide excess; NE, nuclear extract; pCMV, CMV promoter; PKA, protein kinase A; prom, promoter; qPCR, quantitative PCR.