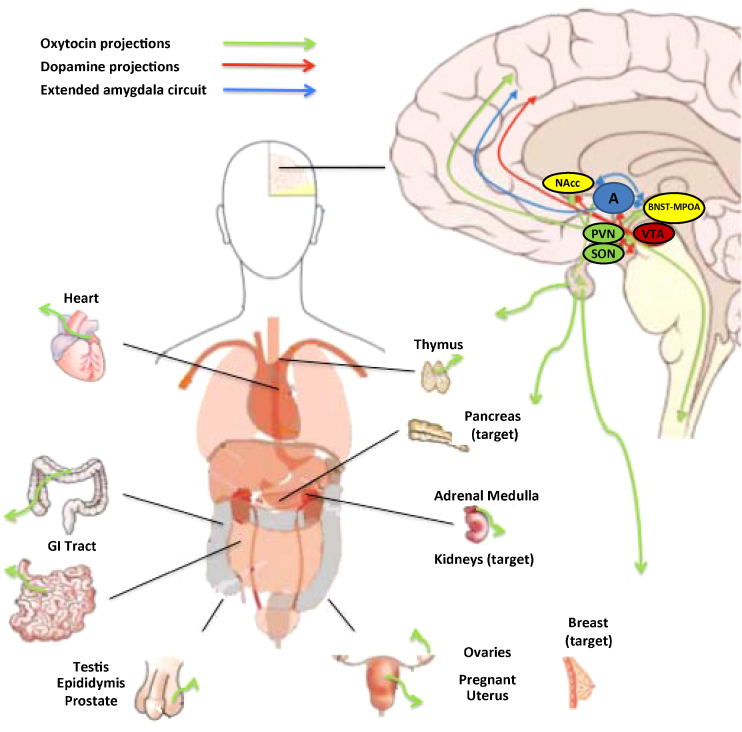
Fig. 1.
Central and peripheral sites of oxytocin (OT) release. Within the brain, OT is released from the paraventricular (PVN) and supraoptic (SON) nuclei of the hypothalamus, and to a lesser extent, the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, spinal cord and anterior commissural nucleus. Central OT projections are pictured in green. Peripheral sources of OT include OT released into circulation via the posterior pituitary as well as numerous sites outside of the brain, including the heart, thymus, gastrointestinal tract, testis, epididymis, prostate, pregnant intrauterine tissue, ovaries, and adrenal medulla. The breast, pancreas and kidney are peripheral OT targets. NAcc = nucleus accumbens; MPOA = medial preoptic area; BNST = bed nucleus of stria terminalis; VTA = ventral tegmental area; A = amygdala.