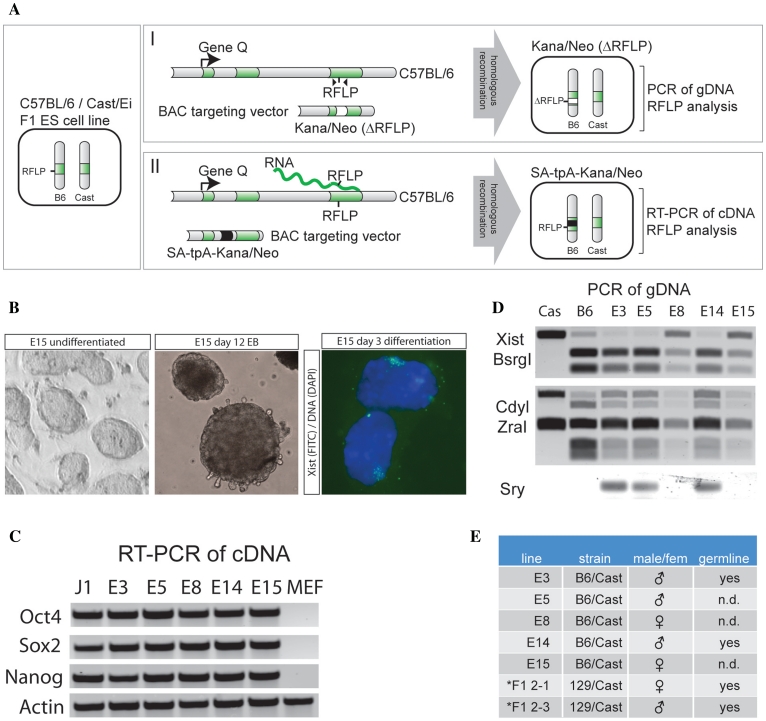
Figure 1.
Two approaches of a new strategy for manipulation of hybrid mouse ES cell lines. (A) Schematic overview of RFLP mediated BAC targeting of hybrid C57BL/6/Cast/Ei ES cells. Chromosomes from C57BL/6 are indicated with B6 and from Cast/Ei with Cast. Exons of the gene of interest are indicated in green, the kanamycin/neomycin resistance cassette in white, and the transcription stop cassette in black. (B) C57BL/6/Cast/Ei hybrid ES cells show proper ES cell morphology (left panel), are able to differentiate in vitro in EBs (middle panel), and female lines can initiate XCI upon differentiation (right panel, showing Xist RNA labeled in FITC, and DNA stained with DAPI). (C) RT–PCR of pluripotency genes. The generated C57BL/6/Cast/Ei ES cells (E3–E15) express the pluripotency factors Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog. J1 is a male control ES cell line, MEFs were used as negative control, and Actin is a control mRNA. (D) PCR amplification of gDNA of different C57BL/6/Cast/Ei ES cell lines (E3–E15) and control gDNA (Cas and B6), and digestion with restriction enzymes identifying allele specific products for Xist (X-encoded, BsrGI, top panel), Cdyl (autosomal, ZraI, middle panel) and PCR amplification of Sry (Y-encoded, bottom panel). (E) Table summarizing the characteristics of the C57BL/6/Cast/Ei ES cell lines analyzed in this study, and two other polymorphic 129/Sv/Cast/Ei cell lines (Asterisk) that have been used in other gene targeting studies (10).