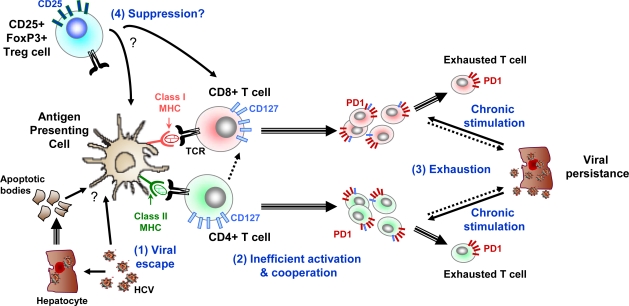
Figure 2.
Examples of mechanisms resulting in impairment of T cell responses leading to chronic HCV infection. Chronic HCV infection is associated with impaired CD8+ T cell responses including reduced cytotoxic potential, reduced secretion of Th1 type cytokines and reduced proliferative capacity in response to ex vivo antigenic stimulation. Four possible mechanisms of T cell response failure are shown here: (1) viral escape with mutations in HLA restricted epitopes impairing antigen recognition, (2) loss of functional CD4+ T cell responses, (3) overexpression of PD1 in CD8+ T cells; when PD1 binds to its ligand PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1), which is preferentially expressed by virus-infected cells, an inhibitory signal is transmitted to CD8+ T cells, resulting in blocking of the T cell receptor-mediated activation signal, (4) induction of regulatory T cells. Arrows with single line indicate functional interactions while arrows with double lines indicate cell differentiation.