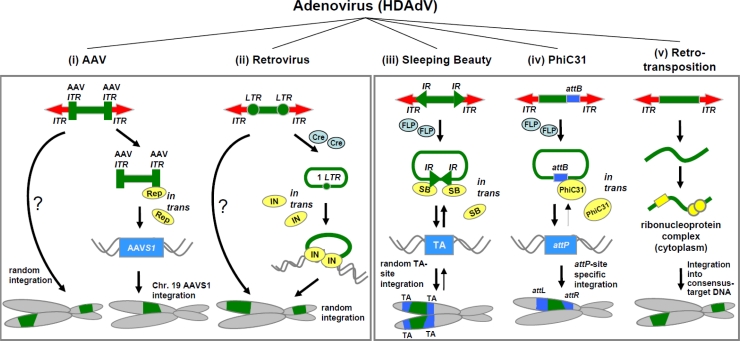
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of all integrating hybrid vector systems based on helper- dependent adenoviral vectors (HDAdV) as delivery vehicles (i–v). The transgene expression cassette (shown in green) and components for somatic integration are co-delivered using the recombinant adenoviral vector. Virus-based integration machineries are shown in the left panel and integration machineries based on non-viral systems are displayed in the right panel. (i) HDAdV/adeno-associated virus (AAV) hybrid vectors integrate into the host genome randomly via AAV internal terminal repeats (ITRs). Rep-Protein expressed in trans provided by a second vector mediates site-specific integration after binding to AAV-ITRs and to the AAV integration site S1 (AAVS1), located on the human chromosome 19. (ii) HDAdV/retrovirus (RV) hybrid vectors integrate transgene expression cassettes flanked by retroviral long terminal repeats (LTRs) directly or after circularization from the adenoviral vector genome mediated by Cre recombinase provided in trans. When the retroviral integrase (IN) is supplied in trans, the integration complex triggers the random insertion of the transgene into the host genome. (iii) For HDAdV/Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposase hybrid vectors the transgene is flanked by inverted repeats (IR) as a recognition site for the Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposase. SB is provided in trans together with Flp recombinase. When Flp mediates circularization of the DNA and therefore mobilization of the transposon from the HDAdV genome, SB binds to the recognition sites and integrates the transposon including the transgene randomly into the TA-sites of the host genome. This process is reversible. (iv) For the HDAdV/PhiC31 integrase hybrid vector system, the vector DNA harbours the PhiC31 recognition site attB within the therapeutic transgene. When PhiC31 protein is provided in trans, it mediates integration into a limited number of pseudo attP sites in the mammalian genome by unidirectional recombination. The circular form of the PhiC31 substrate is released from the adenoviral vector genome by Flp recombinase. At the time it is not clear whether this step is required. (v) Retrotransposition from the adenoviral vector genome is based on the interspersed element L1. After transduction of the target cell L1 and transgene is described and RNA leads to the generation of ribonucleoprotein structure in the cytoplasm. This complex is then imported into the nucleus for somatic integration into a consensus genomic target DNA.