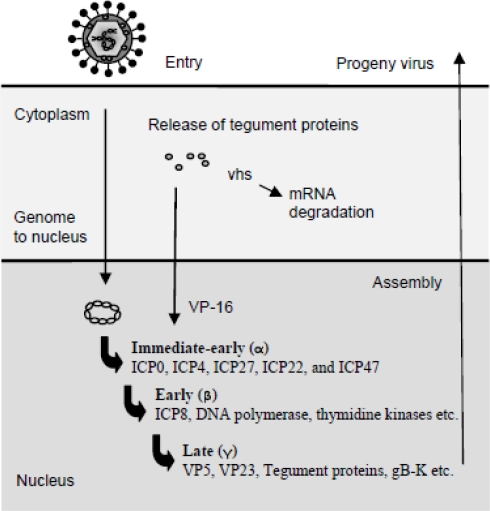
Figure 2.
The replication cycle of HSV. After virus entry, the viral capsid is transported to the nucleus and the genome released into the nucleus through nuclear pores. Viral tegument proteins released into the cell support IE gene transcription or mediate takeover of the cell. The IE proteins are mainly trans-activators that enhance the expression of E genes, which primarily encode enzymes involved in virus DNA replication. Eventually, the L genes are expressed and new virus particles are assembled, matured, and released from the cell, either by cell lysis, endocytosis, or cell-cell fusion.