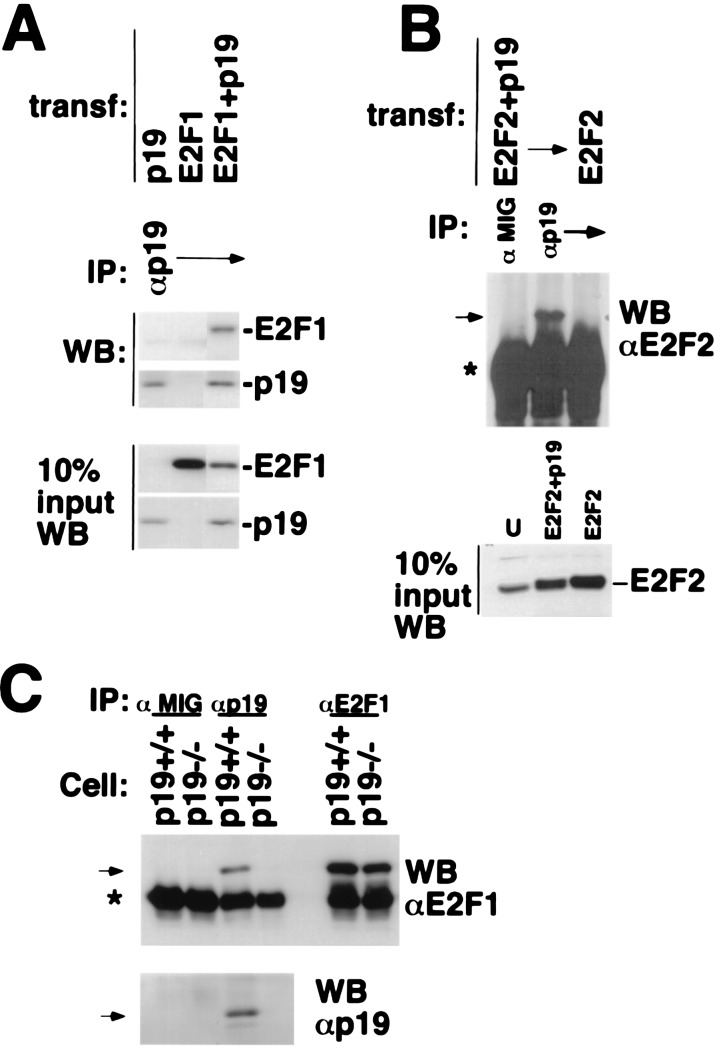
Figure 3.
p19/E2F1 and E2F2 interactions. (A and B) p19ARF interacts with E2F1 and E2F2. U2OS cells were transfected with plasmids encoding p19ARF, HA-E2F1, or HA-E2F2, as indicated. Cell extracts were prepared and then immunoprecipitated with antibody to p19ARF (AEC40). HA-E2F1, HA-E2F2, and p19ARF, present in the p19ARF immunoprecipitates, were analyzed by Western blotting for E2F1 (C20/E2F1), E2F2 (C20/E2F2, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), and p19ARF (AEC40), respectively. In A and B, 10% of each cell extract used for the immunoprecipitations was directly analyzed for relevant protein abundance by Western blotting, with the antibodies above for E2F1, E2F2, or p19ARF. (C) Endogenous p19ARF binds to E2F1. Cell extracts derived from asynchronously growing, immortalized murine p19ARF+/+ (also p53 null) or p19ARF−/− MEFs were immunoprecipitated with antibody to p19ARF (AEC40) or E2F1 (C20) or with mouse IgG (Cappel, negative control). E2F1 and p19ARF present in the p19ARF immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting for E2F1 (C20) and p19ARF (AEC40). Specific bands are indicated by arrows. The asterisk indicates the Ig heavy chain.