Figure 4.
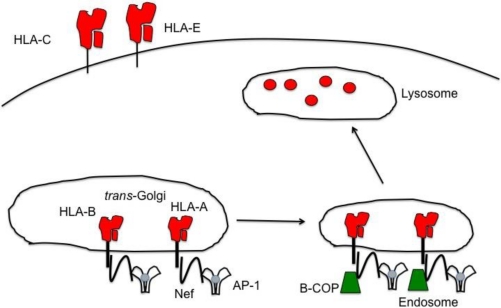
HLA-A and -B are down modulated by HIV Nef, removing an inhibitory signal for NK cells. HIV-1 Nef selectively down modulates HLA-A and -B, but leaves HLA-C and -E on the infected cell surface. Nef re-routes both HLA-A and -B from the TGN to endosomes and eventually to lysosomes for the degradation of the MHC-I molecules. Nef is able to bind to both the tail of the MHC-I molecules as well as the trafficking molecule, AP-1, to facilitate the transport of HLA-A and -B to the endosomes. Once in the endosome, Nef recruits β-COP for further transport into lysosomes. The down modulation of HLA-A and -B removes the inhibitory ligands for the NK cell inhibitory receptor KIR3DL2 and KIR3DL1, respectively. Yet, because Nef is unable to down modulate HLA-C and -E, NK cells expressing inhibitory receptors for these two MHC-I molecules will inhibit NK cell degranulation of HIV infected cells.