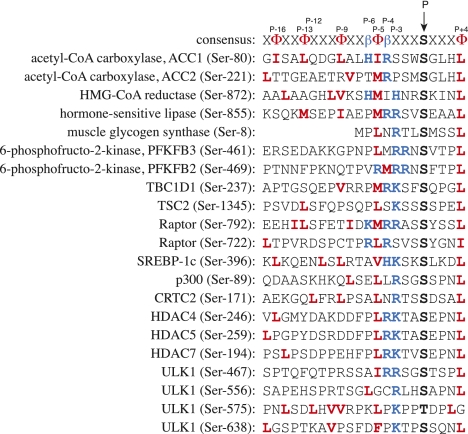
Figure 2.
Alignment of consensus site for recognition of substrates by AMPK (Scott et al. 2002) with the sequences (from humans) of some established physiological substrates. In the consensus sequence, hydrophobic residues are represented by Φ and basic residues are represented by β. AMPK phosphorylates serine residues (threonine also allowed) in the context of hydrophobic residues (in bold, red) at P-5 (usually M or L, but I, V, or F also allowed) and P+4 (usually L, but I, M, F, V, Q, or N allowed), and basic residues (in bold, blue; usually R, but K or H allowed) at P-4, P-3, or both. Another basic residue at P-6 is also a positive determinant, although not essential (Scott et al. 2002). Some substrates (e.g., ACC1) also have hydrophobic side chains at regular spacings of three to four residues (bold, red) running in an N-terminal direction from P-5, which form an amphipathic helix. This is clearly not essential, since the sequence of muscle glycogen synthase starts at P-7. Note that one substrate (PFKFB2) still has a βΦβ motif, but this is at P-5/P-4/P-3 rather than the more common P-6/P-5/P-4.