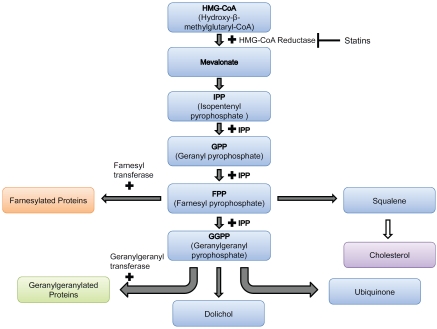
Figure 1.
HMG-CoA is reduced to mevalonate, which is converted into 5-carbon units (C5), called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP). Two C5 units combine to form a C10 compound, geranyl pyrophosphate, which in turn combines with IPP to form the C15 compound farnesol pyrophosphate (FPP). FPP is a common intermediate for the biosynthesis of cholesterol, dolichol and ubiquinone as well as protein isoprenylation. FPP combines with IPP to form the C20 all-trans-geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). The isoprenoids FPP and GGPP are transferred by farnesyl and geranylgeranyl protein transferases respectively to various proteins, such as small GTP-binding proteins, for targeting and activation. Statins inhibit the reduction of HMG-CoA to mevalonate by preventing its binding to HMG-CoA reduc-tase, and hence statin treatment precludes all these events.