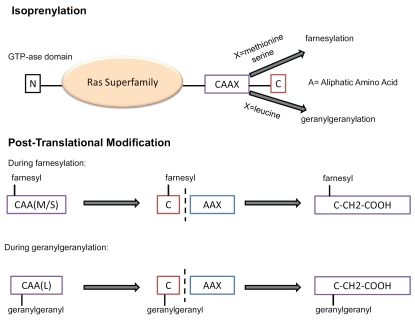
Figure 4.
Mechanism of prenylation of the Ras superfamily GTPases by farnesyl pyrophosphate and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. (upper) Prenylated members of the Ras superfamily are characterized by a CAAX motif at their C-terminal, where A is any aliphatic amino acid and X is a COOH-terminal amino acid that specifies which prenyltrans-ferase will act. Although recent experiments suggest more complex relationships, it is generally believed that CAAX farnesyltransferase preferentially recognizes methionine or serine at the X position and CAAX geranylgeranyl trans-ferase prefers leucine at the X position. For farnesylation, X=methionine or serine whereas for geranylgeranylation, X = leucine. (lower) During post-translational modification, a farnesyl or geranylgeranyl group is first attached to the cysteine group, then the AAX sequence is cleaved and the isoprenylated cysteine is carboxymethylated.