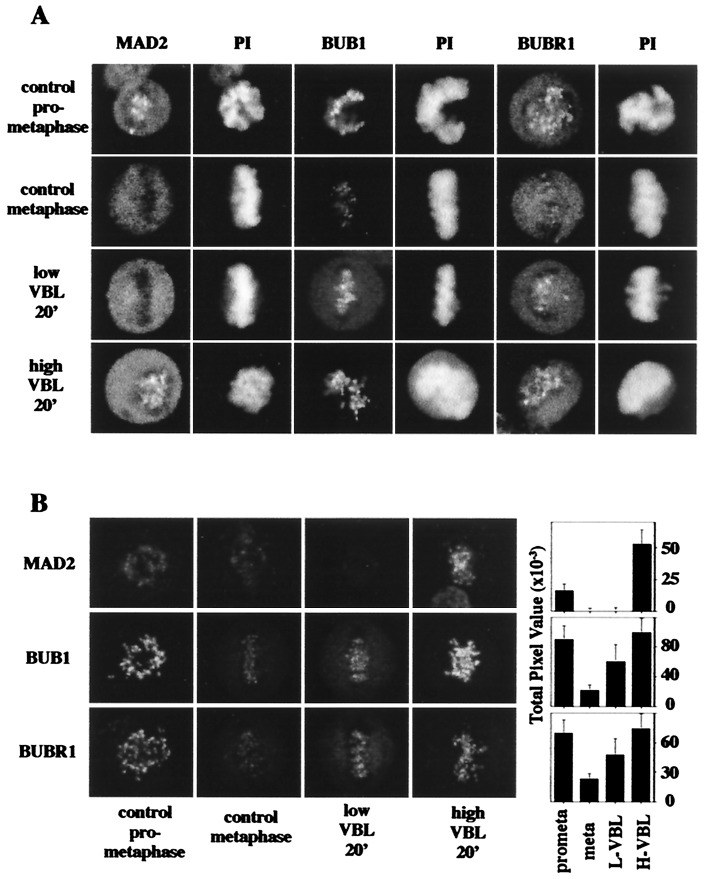
Figure 2.
bub1 and bubR1, but not mad2, respond to the absence of spindle tension by binding to kinetochores. (A) mad2 is absent from kinetochores that have attached microtubules and is insensitive to loss of tension by the addition of 6.7 nM VBL for 20 min. In contrast, mad2 reassociates with kinetochores when attachment is abolished by the addition of 0.5 μM VBL. bub1 and bubR1 are minimally detectable at kinetochores of control metaphase cells but reassociate at kinetochores of metaphase arrays when tension is suppressed by the addition of 6.7 nM VBL or if microtubule attachment is abolished by the addition of 0.5 μM VBL. Results were consistent in several independent experiments and (for bub1) with use of two distinct antibodies (data not shown). For each antigen, all images were collected with a confocal microscope by using constant settings established by imaging control metaphases. (Bar = 5 μm.) (B) Levels of antigens were quantitated for different conditions by using the photon counting mode of the confocal microscope. (Left) The images shown were collected in photon-counting mode at identical machine settings for each antigen. (Right) Compiled data for each of the different conditions with at least 300 kinetochores counted for each data set. Standard deviations were as indicated.