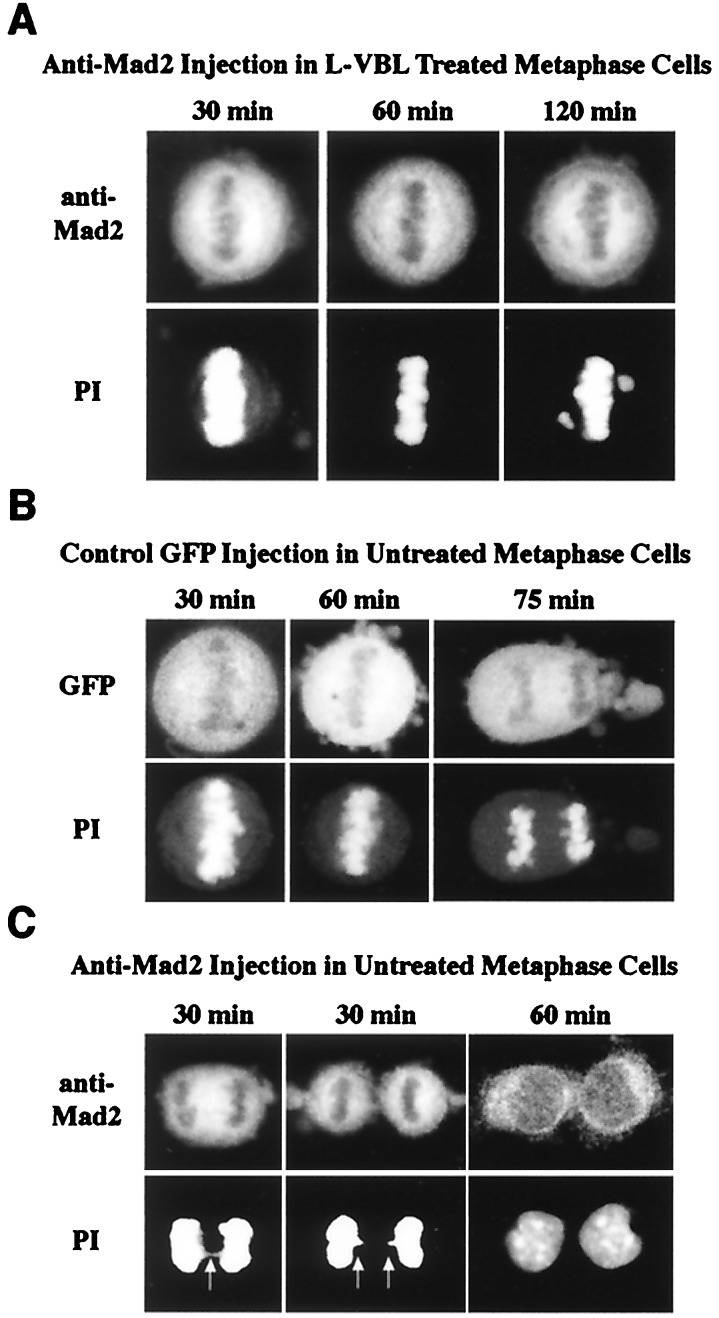
Figure 4.
Response of VLB-treated HeLa to anti-mad2 microinjection. Immunofluorescence micrographs show the result of microinjection of either GFP or anti-mad2 antibody. (A) Cells pretreated for 20 min with low VBL (L-VBL) remain in metaphase configuration for at least 2 h (the last time point taken) after microinjection of anti-mad2 antibody. (B) GFP microinjection was performed as a positive control in untreated metaphase cells. Shown are representative cells that remain at metaphase for 30 and 60 min, respectively, after microinjection. At later times (an anaphase at 75 min is shown here), cells progress to anaphase and exit mitosis. (C) Anti-mad2 microinjection of untreated metaphase cells. In contrast to GFP controls, there is a rapid progression through anaphase and cleavage. Representative cells are shown here 30 min after microinjection in late anaphase and telophase, respectively. The anaphase cells both show evidence of chromosome bridging (arrows), indicating premature entry into anaphase (the propidium iodide stain in both 30-min images has been enhanced to make the bridging visible). GFP or anti-mad2 labels positively identify those cells that had been successfully microinjected. PI, propidium iodide stain to assess the status of the chromosomes after microinjection.