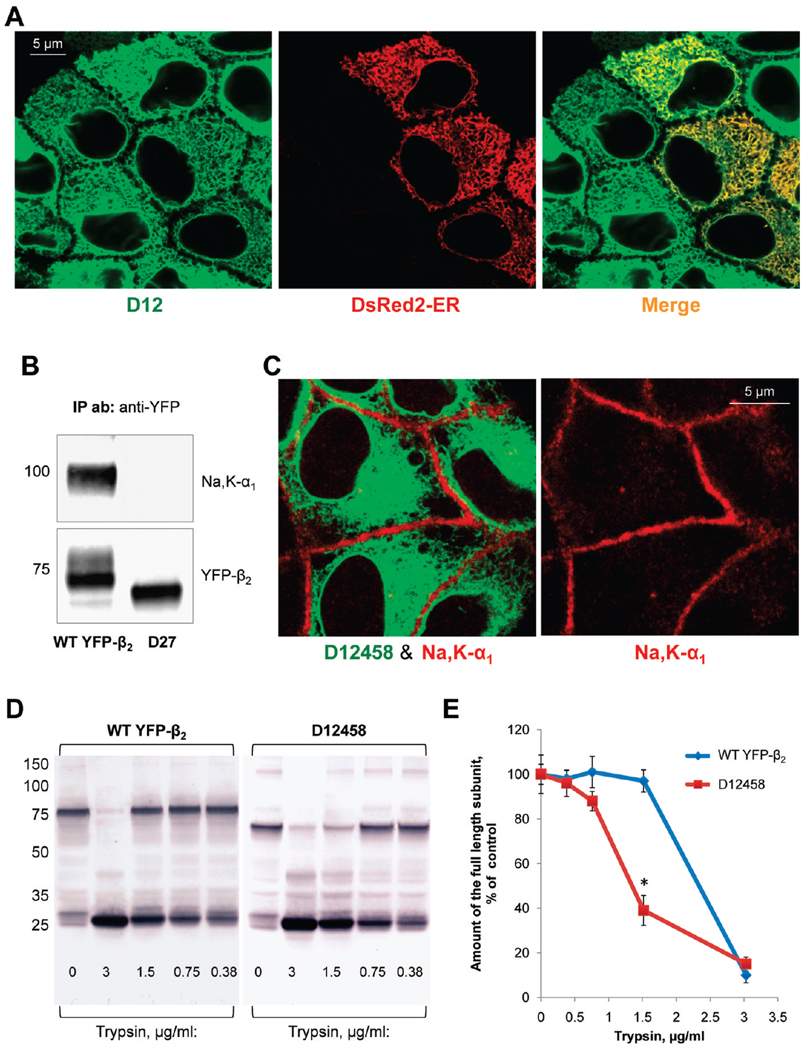
FIGURE 6.
Mutation of particular N-glycosylation sites in the β2 subunit of the Na,K-ATPase impairs normal folding of the subunit and prevents its assembly with the α1 subunit. (A) TheD12 mutant of YFP-β2 (green) is colocalized with the ER(red) as detected by transient expression of the fluorescent ER marker, DsRed2-ER, in the mutant-expressing cells. (B) Wild-type YFP-β2 and its D27 mutant were immunoprecipitated using a polyclonal antibody against YFP from the respective total cell lysates. Precipitated YFP-linked proteins (bottom) and the coprecipitated Na,K-ATPase α1 subunit (top) were analyzed using monoclonal antibodies against YFP and the Na,K-ATPase α1 subunit, respectively. The endogenous Na,K-ATPase α1 subunit is coprecipitated with wild-type YFP-β2, but not with its D27 mutant. (C) The YFP-linked mutant of the β2 subunit, D12458, shows no colocalization with the α1 subunit as detected by immunostaining of the mutant-expressing cells using the monoclonal antibody against the Na,K-ATPase α1 subunit. (D) Confluent monolayers of the cells expressing either wild-type YFP-β2 or its D12458 mutant were incubated in the presence of 100 µg/mL deoxymannojirimycin, the inhibitor of N-glycan processing, for 48 h to prevent heterogeneity of N-glycans. After cell lysis, the whole cell lysates (3 mg/mL) were incubated without or with trypsin at the indicated concentration for 30 min. The products of tryptic digestion were analyzed by immunoblotting using the antibody against YFP. (E) Densitometric quantification of the full-length subunit band at various trypsin concentrations in three parallel experiments shown in panel D indicates that D12458 is more susceptible to digestion by trypsin than the wild-type subunit.