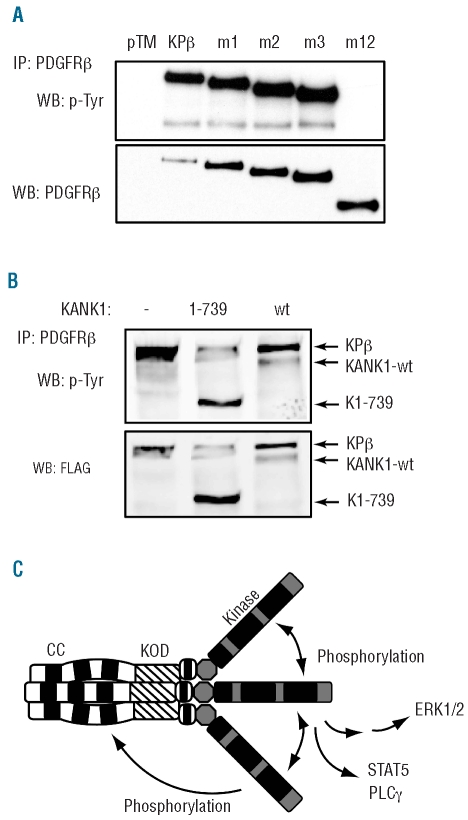
Figure 5.
The KANK1 part of KPβ is required for autophosphorylation and provides additional phosphorylated tyrosine residues. (A) Lysates of Ba/F3 cells expressing the indicated mutant were immunoprecipitated with anti-PDGFRβ antibodies and analyzed by western blot with anti-phosphotyrosine or anti-PDGFRβ antibodies. Alternatively, blots were analyzed using quantitative Odyssey technology, which indicated that normalized PDGFRβ phosphorylation (calculated as the phosphotyrosine to PDGFRβ signal ratio) was decreased by 64% in m1, 65% in m2 and 58% in m3 compared to KPβ. (B) HEK-293T cells were transfected with KPβ together with KANK1, K1-739 or an empty vector. Cells were treated for 4 h with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (20 μM) to increase KANK1 expression level. KPβ was immunoprecipitated with anti-PDGFRβ antibodies and blotted sequentially with anti-phosphotyrosine and anti-FLAG antibodies. (C) Model for KPβ oligomerization, phosphorylation and signaling. See Figure 3 for abbreviations.