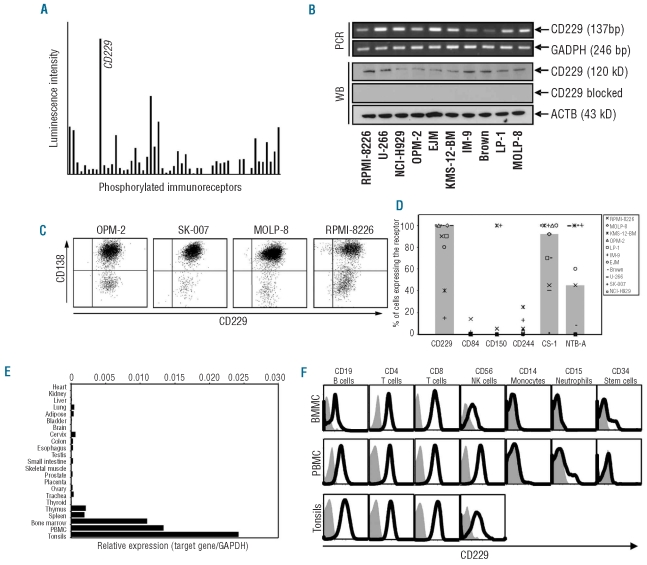
Figure 1.
CD229 is expressed on myeloma cell lines and primary tumor cells from MM patients. Expression of 59 immune-related surface molecules in lysates of the MM cell line MOLP-8 was analyzed using the human phospho-immunoreceptor array. Bars indicate the mean luminescence intensity of spots representing individual phosphorylated immunoreceptors after subtraction of background levels measured for the internal negative control (A). RNA expression of CD229 was demonstrated by reverse transcriptase-PCR in ten different myeloma cell lines and constant expression of CD229 at the protein level was confirmed using western blot. Housekeeping genes GAPDH and β actin (ACTB) were used as internal controls for PCR and western blot (B). Strong surface expression of CD229 was detected on CD138-positive conventional myeloma cell lines and the CD138-negative subpopulation using flow cytometry (C). Compared to other members of the SLAM family, CD229 showed the strongest and most consistent surface expression on 11 myeloma cell lines as determined by flow cytometry. The percentages of positive cells among a given cell line (symbols) and median expression (gray bars) are shown (D). RNA expression of CD229 was measured in various human tissues using real-time PCR. Highest copy numbers were found in tonsillar tissues (mean expression of 6 patients), PBMC (mean expression of 4 donors) and bone marrow mononuclear cells (mean expression of 10 donors), while thymus and spleen were only marginally positive and no expression was found in any other tissue. Bars indicate expression of CD229 as normalized for copy numbers of the housekeeping gene GAPDH (E). Leukocyte subsets among PBMC, bone marrow mononuclear cells and tonsillar cells were analyzed for CD229 expression by flow cytometry. Results are representative of analyses of four separate donors (F).