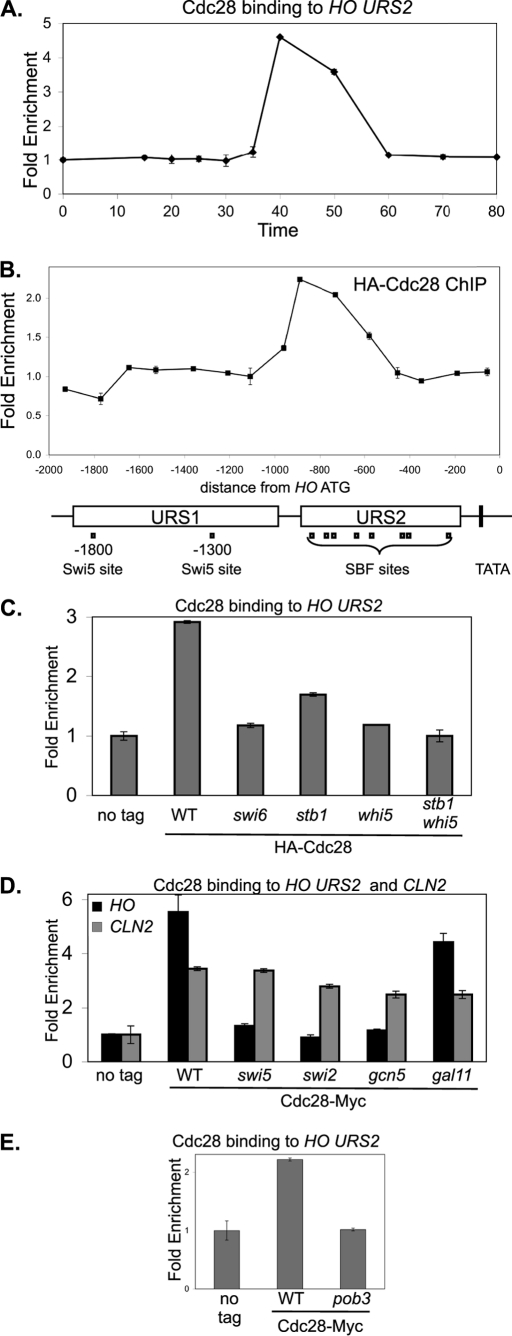
FIGURE 6.
Cdc28 kinase is recruited to HO URS2. A, strain DY6669 (GALp::CDC20 SWI4-Myc) with HA-CDC28 on a YCp-KanMX plasmid was synchronized, and ChIP samples were taken at various times following release from CDC20 arrest. Cdc28 binding to HO URS2 was measured with primers that amplify from −825 to −489. B, ChIP samples prepared from logarithmically growing strain DY150 with either a YCp-KanMX(HA-CDC28) plasmid or an empty YCp-KanMX vector were synchronized, and Cdc28 binding was analyzed with 15 sets of PCR primers across the HO promoter. URS1-, URS2-, Swi5-, and SBF-binding sites are shown for the HO promoter, where the ATG represents +1 and the transcription start site is at −20. C, ChIP experiments were performed with logarithmically growing untagged control strains (DY150, wild type; DY6999, swi6; DY13454, stb1; DY9559, whi5; and DY13640, whi5 stb1) and CDC28-Myc strains (DY13020, wild type; DY13723, swi6; DY13729, stb1; DY13731, whi5; and DY13733, stb1 whi5). Cdc28 binding to HO URS2 was measured with primers that amplify from −825 to −489. D, ChIP experiments were performed with logarithmically growing strains (DY150, wild type; DY161, swi5; DY5270, swi2Δ; DY5925, gcn5; and DY5628, gal11) containing either a YCp-KanMX(HA-CDC28) plasmid or an empty YCp-KanMX vector. Cdc28 binding to HO URS2 was measured with primers that amplify from −825 to −489 and binding to CLN2 with primers that amplify from −661 to −379. E, ChIP experiments were performed with logarithmically growing untagged control strains (DY150, wild type; DY7379, pob3(L78R)) and CDC28-Myc strains (DY13020, wild type; DY13527, pob3(L78R)), grown at 25 °C. Cdc28 binding to HO URS2 was measured with primers that amplify from −825 to −489.