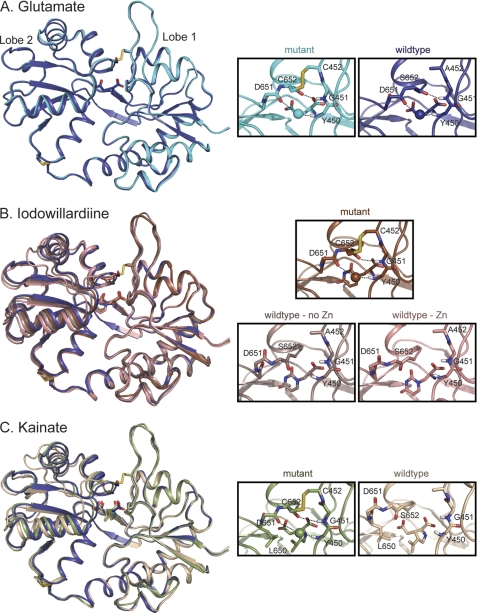
FIGURE 2.
Crystal structures of wild type and A452C/S652C mutant GluA2 LBD bound to glutamate (A), iodowillardiine (B), and kainate (C). The right panels show the agonist binding site. A, glutamate. The structure of wild type GluA2 bound to glutamate (Protein Data Bank code 3DP6; B protomer, 24) is shown in dark blue and the A452C/S652C mutant (Protein Data Bank code 3T93) is shown in cyan. The water molecule involved in the Asp-651–Tyr-450 H-bond is shown in the same color as the backbone in all parts of this figure. The Cys-452–Cys-652 disulfide bond is clearly present in the mutant. B, iodowillardiine. The structure bound to glutamate is shown in blue to indicate the orientation of a fully closed lobe. The iodowillardiine-bound structures are shown in shades of brown/pink. Two wild type iodowillardiine-bound structures are shown, one crystallized in the presence of zinc (Protein Data Bank code 1MY4, A protomer; 20) and one in the absence of zinc (Protein Data Bank code 1MQG, A protomer; 12). Both are shown to illustrate the variability seen in different crystal structures. The mutant structure is more closed and the Asp-651-H2O-Tyr-450 and Cys-652–Gly-451 H-bonds are clearly present as is the Cys-452–Cys-652 disulfide bond (Protein Data Bank code 3T96). C, kainate. The glutamate-bound structure is shown in dark blue, and the wild type kainate-bound structure is shown in tan (Protein Data Bank code 1FW0; 3). As seen for iodowillardiine, the A452C/S652C mutant structure (shown in green) is more closed and the Asp-651–H2O–Tyr-450 and Cys-652–Gly-451 H-bonds are clearly present as is the Cys-452–Cys-652 disulfide bond (Protein Data Bank code 3T9H). Note the change in the rotameric state of the side chain of Leu-650.