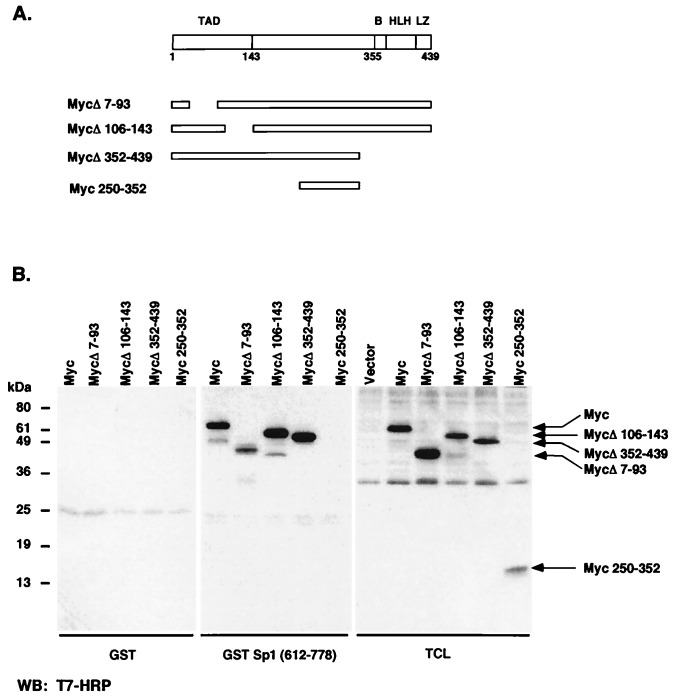
Figure 5.
The central region of c-Myc protein between amino acids 143 and 352 is involved in interaction with Sp1. (A) The structural domains of c-Myc and the c-Myc mutants used in this work are diagrammed. Domains include the transcriptional activation domain (TAD), a basic region (B), a helix–loop–helix motif (HLH), and leucine zipper domain (LZ). (B) 293 cells were transfected with expression constructs for T7-tagged c-Myc, the Myc deletion mutants MycΔ7–91, MycΔ106–143, and MycΔ352–439, and the Myc fragment 250–352 and harvested 48 h after transfection. Pull-down assays were performed by incubating lysates with GST or GST-Sp1-(612–778) for 1 h at 4°C followed by incubation with glutathione beads for 1 h. Bound proteins were subjected to SDS/PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti-T7 antibody.