FIG. 4.
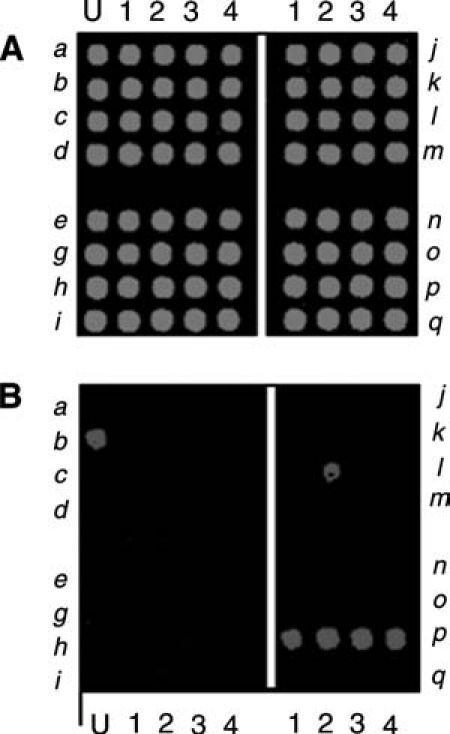
Staphylococcal enterotoxin microarray. This microarray was designed to detect 16 S. aureus enterotoxin genes (sea-seq). The microarray is composed of four sections, each representing four enterotoxin genes (each row is one gene). Each gene is detected by four unique probes (the four spots in each row). The first column labeled U is printed with a spotting solution that provides an indicator of the microarray position on the substrate. The upper section (A) is an image of the signal from the quality control (QC) probes and the lower section (B) is an image of the signal from the data probes for the enterotoxin genes. The spots for the sea–sei genes are in the left block and the sej–seq genes are in the right block, with each gene represented by four unique spots. (A) The QC scan of the array in which each spot of the array shows a signal because each spot contains a small amount of a QC oligoprobe, which hybridizes with a Cy3-labeled QC oligonucleotide spiked in the target mixture. The QC scan is excited using the 543 nm laser. (B) The data scan for a particular sample generated by amplifying genomic DNA from S. aureus strain N315 using primers specific for enterotoxin p (sep). The PCR product was labeled with Cy5. The data scan was done using 632 nm excitation.
