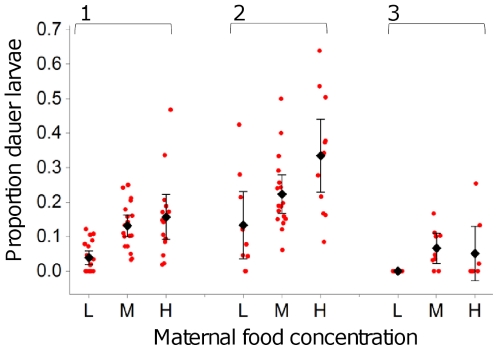
Figure 3. Maternal food availability affects development fate.
Jitter plot showing the proportions of the L1 progeny of mothers from high (H), medium (M) and low (L) maternal food concentrations that developed as dauer larvae in three independent experiments (1–3). The mean proportion (±95% confidence interval) of L1 progeny that developed as dauer larvae is also shown for each treatment. In all cases High maternal food availability was 10% w/v E. coli. Medium maternal food availability was 2.5% w/v E. coli for assays 1 and 3, and a combination of 2.5% and 5% w/v E. coli treatments for assay 2. Low maternal food availability was 1.25% w/v E. coli for assays 2 and 3, and a combination of 1.25% and 0.625% w/v E. coli treatments for assay 2. Mean proportions were calculated from 8–20 plates/treatment (median 12).