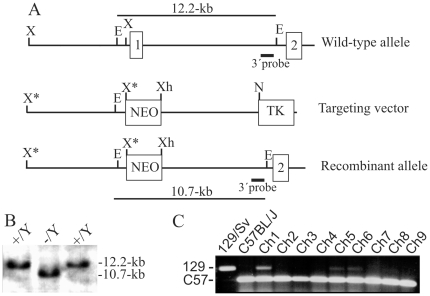
Figure 5. Targeting disruption of the Vsig1.
(A) Structure of the wild-type, targeting vector and recombinant allele are shown together with the relevant restriction sites. A 2.5-kb genomic fragment containing exon 1a was replaced by a pgk-neo selection cassette (NEO). The probe used and predicted length of the EcoRI restriction fragment in Southern blot analysis are shown. TK, thymidine kinase cassette; E, EcoRI; X, XbaI; X*, disrupted XbaI site; Xh, XhoI. (B) Blot with EcoRI-digested genomic DNA of recombinant ESC clones was probed with the 3′ probe shown in panel A. The external probe recognized only a 10.7-kb fragment of recombinant allele in Vsig1−/Y ESCs and a 12.2-kb fragment of the wild-type allele in Vsig1+/Y ESCs. (C) PCR assay using microsatellite markers was performed to determine the degree of chimerism in the stomachs of chimeric male mice. The 129- and C57-specific fragments were amplified using DNA of the 129/Sv and C57BL/6J mouse strains, and stomach isolated from different chimeric males (Ch).