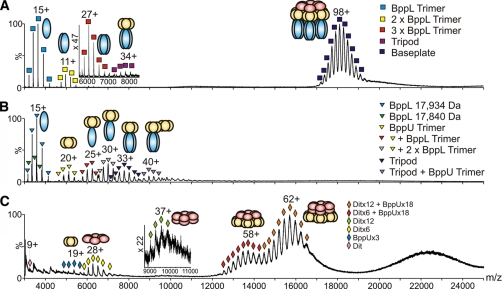
Fig. 2.
ESI-MS spectra of TP901–1 baseplate and sub-complexes. A, TP901–1 baseplate (TP1). The measured mass of the intact complex centered at m/z 18,000 (navy blue squares) is 1,769,204 Da, consistent with a stoichiometry of [6×ORF46 + 18×ORF48 + 54×ORF49]. Also identified are Tripods with a mass of 265,995 Da (magenta squares; m/z 8000) as well as BppL trimers (54,646 Da), dimer of trimers and trimer of trimers (blue, yellow, and red squares centered at m/z 3500, 5000, and 6000, respectively). Inset: m/z 6000–8000 highlighting the Tripod complex and the BppL trimer of trimers. B, Tripod subcomplex. The Tripod measured mass was 264,088 Da (navy blue triangles; m/z 7500), consistent with a stoichiometry of [3×BppU + 9×BppL]. The presence of BppL trimers and BppU trimers was also detected (blue and yellow triangles centered at m/z 3500 and 5250, respectively) in addition to Tripods lacking one or two BppL trimers and complete Tripods associated with a BppU trimer (gray, red, and violet triangles centered at m/z 7000, 6250, and 9000, respectively). C, Dit-BppU complex. The signals centered at m/z 16,000 (orange diamonds) correspond to a mass of 959,852 Da consistent with a stoichiometry of [12× ORF46 + 18×ORF48]. Another observed species was centered at m/z 14,000 (red diamonds) and had a mass of 784,979 Da consistent with a complex of stoichiometry [6×ORF46 + 18×ORF48]. Also identified are Dit (ORF46) hexamers (measured mass: 175,173 Da, yellow diamonds; m/z 6500), dodecamers (350,348 Da, green diamonds; m/z 9500) and BppU (ORF48) trimers (101,584 Da, pale blue diamonds; m/z 5500). Inset: m/z 9000–11,000 highlighting the Dit dodecamers.