Figure 4.
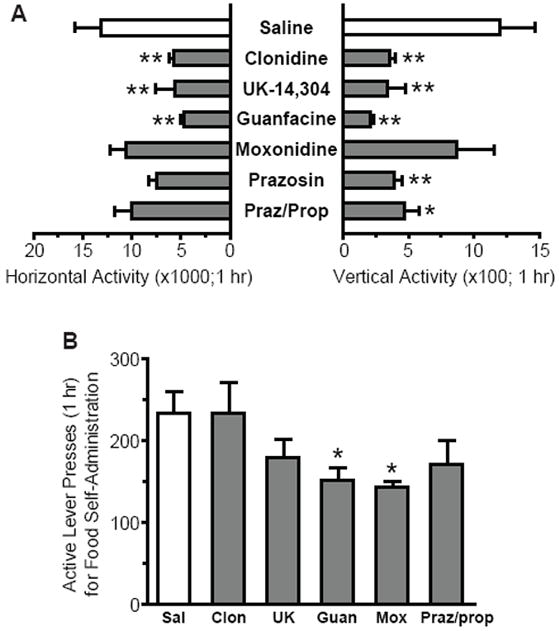
Most adrenergic ligands reduced activity in a novel locomotor chamberwith little effect on food self-administration.(A)Activity (number of beam breaks in 1 hr) was assessed in a locomotor chamber following pretreatment with saline (n=6), clonidine (20 μg/kg; n=7), UK-14,304 (200 μg/kg; n=7), guanfacine (1 mg/kg; n=7), moxonidine (1 mg/kg; n=7), prazosin (3 mg/kg; n=7), or prazosin plus propranolol (1+10 mg/kg; n=7). Horizontal activity was significantly reduced by clonidine, UK-14,304, and guanfacine, as compared to saline (**p<0.01). Vertical activity was significantly reduced by all ligands except moxonidine (*p<0.05, **p<0.01).(B) Food self-administration was tested following pretreatment with saline,clonidine (20 μg/kg), UK-14,304 (200 μg/kg), guanfacine (1 mg/kg), moxonidine (1 mg/kg), or prazosin plus propranolol (1+10 mg/kg) in a within-subject, counterbalanced design (n=8).Guanfacine and moxonidine reduced responding, as compared to saline (*p<0.05).
