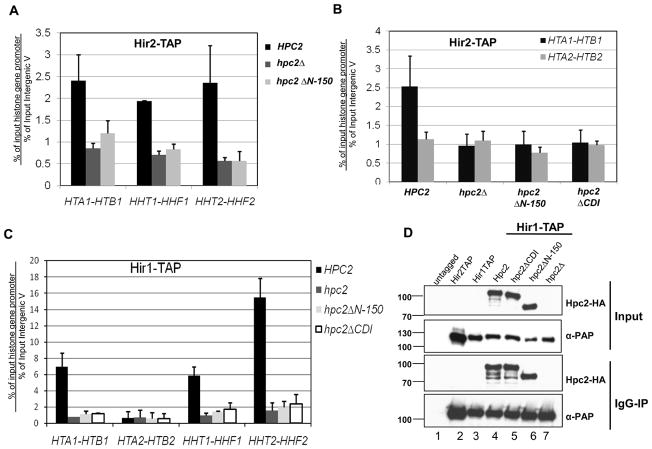
Figure 4. The Hpc2 N-terminal conserved CDI domain is necessary for HIR recruitment at the HIR-dependent histone genes.
(A) The Hpc2 N-terminal region is necessary for the recruitment of the HIR complex to the HIR-dependent histone gene loci. Cells from yeast strain YPP996 (HIR2-TAP) transformed with indicated YCp:URA3 plasmid were analyzed by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) for the association of Hir2-TAP to the indicated histone gene loci, as described in the Material and Methods. Specific primer pairs to the promoter of the indicated histone gene loci were used (primers sequence available upon request). The fold enrichment is calculated as the ratio of percent IP of the indicated region to percent IP of a non-transcribed control region (Inter V). The values shown represent the average and standard errors from three independent experiments. (B) Hpc2 CDI is necessary for association of the HIR complex to HTA1-HTB1 loci. ChIP assay done as in (A) except that YPP996 strain was transformed with the indicated YIp:TRP1 plasmid. (C) The Hpc2 CDI domain is necessary for the association of Hir1-TAP to the HIR-dependent histone gene loci. Cells from yeast strain YPP1213 (HIR1-TAP) transformed with indicated YIp:TRP1 plasmid were analyzed by ChIP for the association of Hir1-TAP to the indicated histone gene loci. The values shown represent the average and standard deviation from two independent experiments. (D) Whole cell extracts were made from the strains used in (C) and other indicated strains. Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed using IgG-sepharose beads and analyzed by Western hybridization with anti-HA and peroxidase anti-peroxidase (α-PAP) antibodies to verify the correct expression and interaction of the indicated Hpc2 wild-type and mutant proteins with Hir1-TAP tagged subunit.