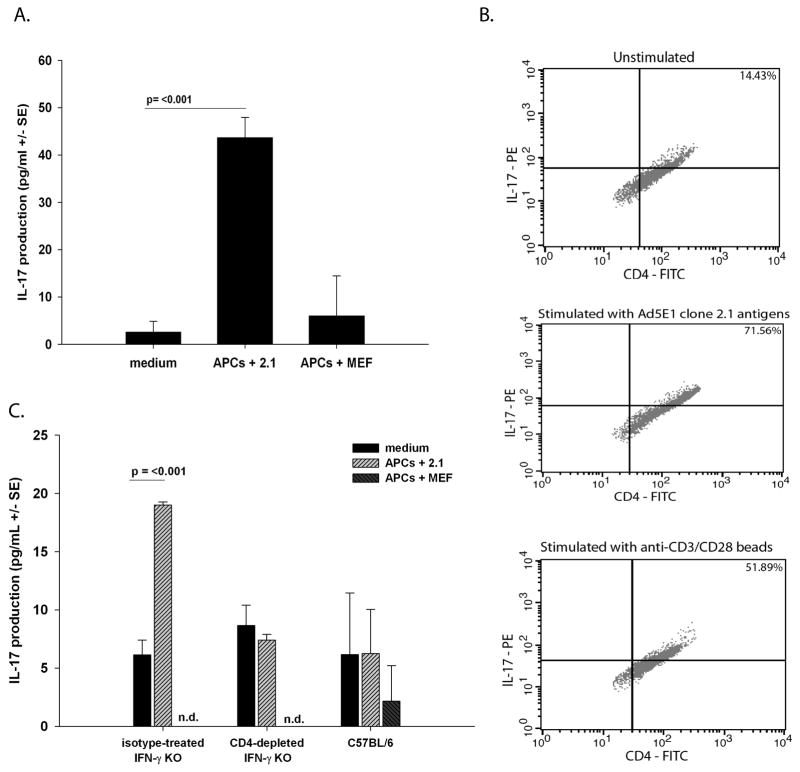
Figure 4. Rejector CD4+ T cells produce IL-17 following stimulation with tumor antigens.
(A) T cells from SC tumor rejector IFN-γ KO mice were cultured with medium alone, Ad5E1 clone 2.1 tumor antigen-pulsed APCs, MEF antigen-pulsed APCs, or anti-CD3/CD28 dynabeads for 5 days at 37 °C. CD4+ T cells were harvested from isotype antibody treated IFN-γ KO mice. Production of IL-17 (pg/ml +/− SE) was determined by ELISA. Data are a representative of two independent experiments. P values < 0.05 were considered significant as determined by Student’s t test. (B) CD4+ T cells were cultured with medium alone (unstimulated) (upper panel), Ad5E1 clone 2.1 tumor antigen-pulsed APCs (middle panel), or anti-CD3/CD28 dynabeads (lower panel) and intracellular stained with anti-IL-17-PE and anti-CD4-FITC. Data are a representative of two independent experiments. (C) Splenocytes were harvested from isotype antibody-treated IFN-γ KO mice, from anti-CD4-treated IFN-γ KO mice or from WT C57BL/6 mice. Production of IL-17 (pg/ml +/− SE) was determined by ELISA. Data are a representative of two independent experiments. P values < 0.05 were considered significant as determined by Student’s t test.