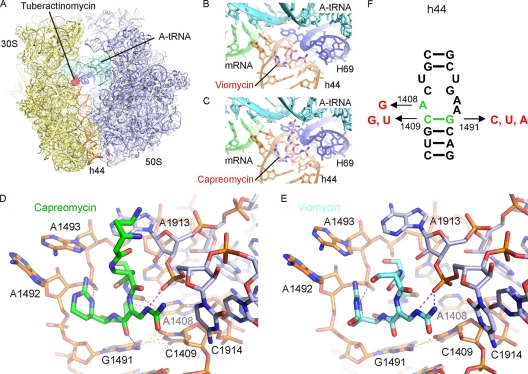
Fig. 1.
Binding site of tuberactinomycins viomycin and capreomycin. (A) Overview of the binding site of the tuberactinomycins (red) at the interface between the small (30S) (yellow) and large (50S) (blue) ribosomal subunits (37). A-tRNA (cyan), P-tRNA (green), and h44 (orange) are in color for reference. (B and C) Enlargement of panel A to show binding site of viomycin (B) and capreomycin (C) to h44 (orange) of the 30S and H69 (blue) of the 50S, with the mRNA and A-tRNA in green and cyan, respectively. (D and E) Interaction of the tuberactinomycins within the ribosomal binding site. Capreomycin (D) (green) and viomycin (E) (cyan) form hydrogen bond interactions (magenta) with h44 of the 16S rRNA (orange) and H69 of the 23S rRNA (blue) (37). Intramolecular hydrogen bonds between rRNA nucleotides are yellow. (F) Secondary structure of decoding site rRNA sequences in the small ribosomal subunit. Nucleotides shown in green represent residues that were exchanged to residues shown in red. rRNA nucleotides are numbered according to the bacterial nomenclature; i.e., to homologous E. coli 16S rRNA positions.