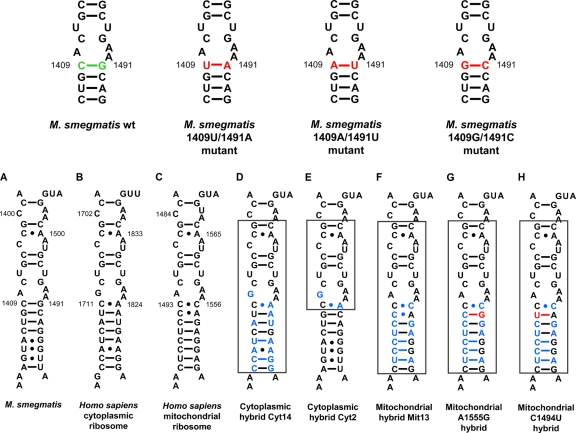
Fig. 2.
(Top) Compensatory mutations in decoding site of bacterial small ribosomal subunit rRNA. Nucleotides shown in green represent residues that were exchanged to residues shown in red. (Bottom) Secondary-structure comparison of decoding site rRNA sequences in the small ribosomal subunit. (A) Decoding region of 16S rRNA helix 44 in wild-type ribosomes of M. smegmatis; rRNA nucleotides are numbered according to the bacterial nomenclature; i.e., to homologous E. coli 16S rRNA positions. (B) Homologous 18S rRNA sequence in human ribosomes; rRNA residues are numbered according to the human cytoplasmic ribosome nomenclature. (C) Homologous 12S rRNA sequence in human mitochondrial ribosomes; rRNA residues are numbered according to the mitochondrial nomenclature. (D to H) Decoding site rRNA of human-bacterial hybrid ribosomes. The transplanted helix is boxed, and nucleotide positions shown in blue represent residues that are specific for human rRNA. Mutations that are associated with hypersusceptibility to aminoglycoside antibiotics, mitochondrial DNA position 1555A→G (G), and 1494C→U (H) are highlighted in red.