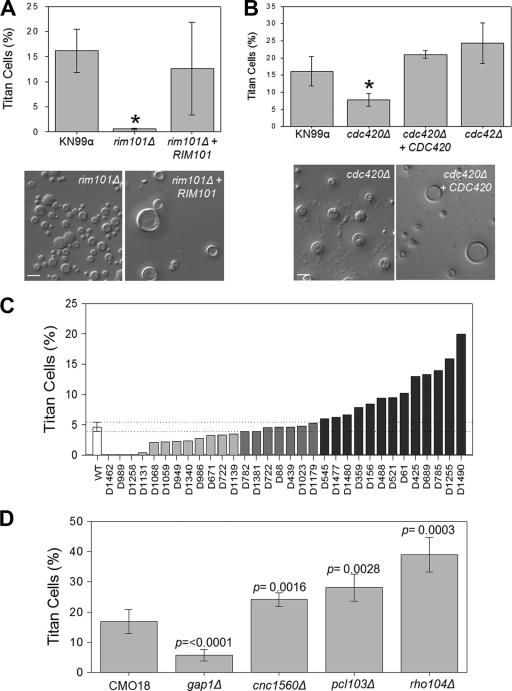
Fig. 5.
Regulators of titan cell signaling. Mice were infected intranasally with 2 × 107 cryptococcal cells. At 3 days postinfection, BAL samples were collected and fixed. Small cells (cell body diameter, <10 μm) and titan cells (cell body diameter, >10 μm) were quantified by microscopy. More than 300 cells were counted per treatment per mouse. (A) The rim101Δ mutant and a complemented (rim101Δ + RIM101) strain were assessed for titan cell formation. Error bars indicate standard deviations for 3 to 5 mice per treatment. The asterisk indicates a significant difference (P < 0.02) from the wild type. (B) cdc420Δ, cdc420Δ + CDC420, and cdc42Δ strains were assessed for titan cell formation. Error bars indicate standard deviations for 3 to 5 mice per treatment. The asterisk indicates a significant difference (P < 0.02) from the wild type. (C) Thirty-two mutant strains were assayed for titan cell formation. The standard deviation (dotted lines) for the wild type (open bar) was used to identify mutant strains that exhibit altered titan cell formation. (D) Four of the mutant strains for which results are shown in panel C were further analyzed for titan cell formation. For all these strains, the levels of titan cell formation are statistically significantly different from that of the wild type (P < 0.02). Error bars indicate standard deviations for 3 to 5 mice per treatment.