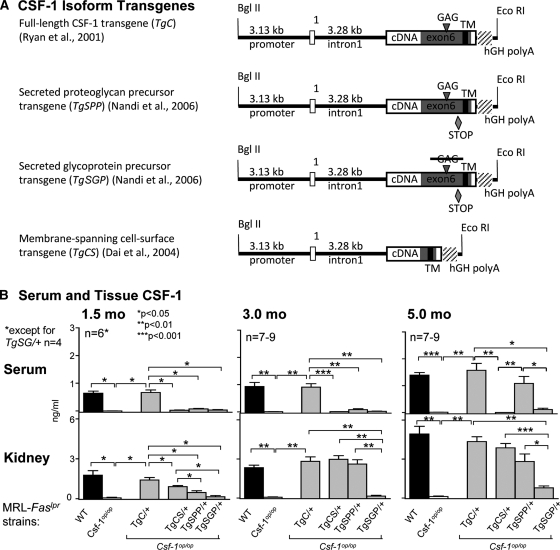
Figure 1.
spCSF-1, but not csCSF-1, contributes to the increase in serum CSF-1, and both are upregulated in the kidney with advancing disease in MRL-Faslpr mice. (A) CSF-1 isoform transgenes driven by Csf1 promoter (3.13 kb) and first intron (3.28 kb). TgC contains the full-length cDNA (exons 1 to 9). The other transgenes are altered as follows. Both TgSPP and TgSGP contain a stop codon at amino acid 456 to ensure that they are secreted. TgSGP has, in addition, a mutation (S276L-G277A) in the unique glycosaminoglycan (GAG) addition site (SGXG/A) to prevent addition of the chondroitin sulfate chain. csCSF-1, incorporated in TgCS results from alternative splicing in exon 6 that removes the GAG addition site and sequences encoding the proteolytic cleavage sites that release the secreted forms from their transmembrane tether (reviewed in reference 12). (B) Serum and kidney CSF-1 levels in TgC/+, TgCS/+, TgSPP/+, and TgSGP/+ mice with advancing lupus nephritis (1.5, 3.0, and 5.0 months of age); MRL-Faslpr mice (WT, wild type) and Csf1op/op mice served as controls. CSF-1 levels in serum and in kidney homogenates determined by ELISA. The values are the means ± SEM.