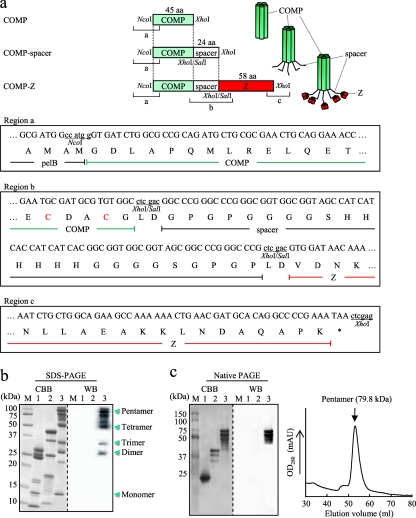
Fig. 2.
Expression of the COMP-based delivery molecules. (a) Schematic drawing of the rat cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP)-derived coiled-coil domain-based constructs: COMP, COMP coiled-coil domain; COMP-spacer, COMP fused to a spacer sequence; COMP-Z, COMP-spacer fused to the Z domain. All constructs were cloned between the NcoI and XhoI sites of pET-22b and were expressed as pelB fusion proteins. The nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequences of the 5′-terminal, junction, and the 3′-terminal regions are shown as regions a, b, and c, respectively. Two inherent Cys residues within the COMP coiled-coil domain (as indicated in region b) are specific sites used for chemical conjugation. (b and c) SDS-PAGE (b) and native PAGE (c) (left) of the affinity-purified COMP (lanes 1), COMP-spacer (lanes 2), and COMP-Z (lanes 3) and size exclusion chromatography of the COMP-Z (c) (right). M, molecular mass marker. The protein bands were either stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) or subjected to Western blotting (WB). For WB, HRP-conjugated goat IgG was applied directly to the blotted membrane for detection of the Z domain-containing proteins.