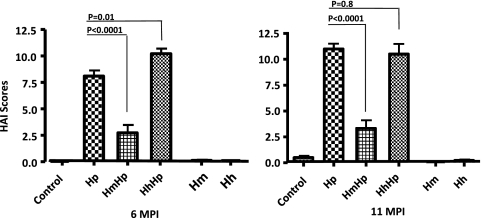
Fig. 2.
Gastric histologic activity index (HAI). For 6 to 11 months, gastric tissues from C57BL/6 mice infected with H. pylori, H. muridarum, or H. hepaticus or from HmHp or HhHp mice (n = 13 to 15 for all groups) were graded for inflammation, epithelial defects, atrophy, hyperplasia, pseudopyloric metaplasia, dysplasia, hyalinosis, and mucous metaplasia. A gastric histologic activity index was generated by combining scores for all criteria except hyalinosis and mucous metaplasia, which may develop irrespective of helicobacter infection. H. muridarum attenuated H. pylori gastritis at 6 and 11 MPI, whereas H. hepaticus enhanced H. pylori gastritis at 6 MPI.