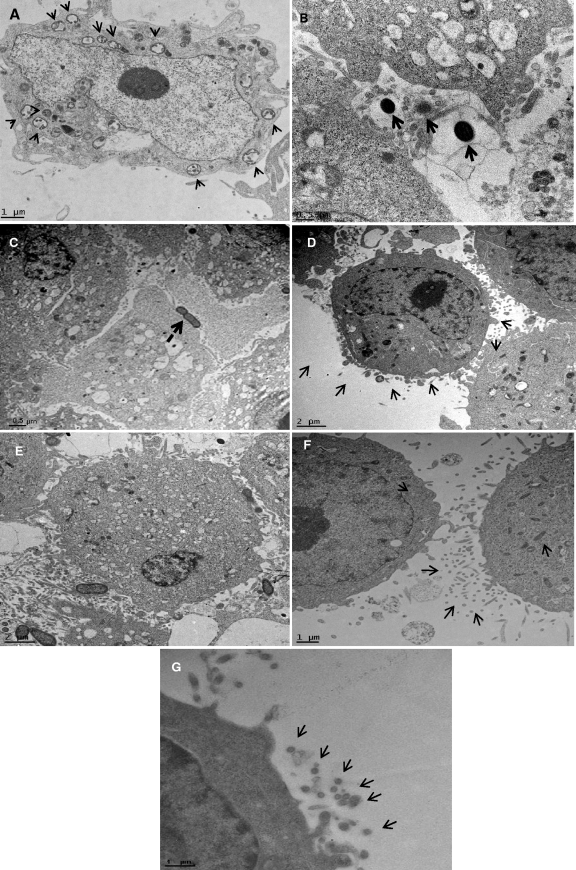
Fig. 8.
Ultrathin sections of the infected epithelial cell monolayer were washed with PBS, fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde, and stained with lead citrate and uranyl acetate. The grids were examined using by the FEI Tecnai G2 transmission electron microscope. Arrows show vesicles in the cytoplasm containing both Filifactor alocis D-62D and P. gingivalis W83. (A) Ultrathin sections of the coculture-infected epithelial cell monolayer at 45 min p.i. Arrows show endocytic vesicles in the cytoplasm containing both bacteria. (B) Monoculture of P. gingivalis W83 at 45 min p.i., showing invading organisms without an external envelope or covering. (C) Monoculture of Filifactor alocis D-62D at 45 min p.i., showing invading organisms without a covering. (D) Invasion by a coculture of F. alocis D-62D and P. gingivalis W83 at 30 min p.i., showing formation of the vesicular covering (arrows). The covering was noticed when the bacteria were in contact with the epithelial cells. Such receptor-mediated endocytosis was found only during coculture. (E) Coculture of P. gingivalis W83 and F. alocis D-62D at 30 min p.i., showing a higher number of invading P. gingivalis W83 cells. (F and G) P. gingivalis W83 monoculture at 30 min p.i., showing cytoskeleton variation through formation of microvilli, filamentous projections of the epithelial cells facilitating invasion by the bacteria.