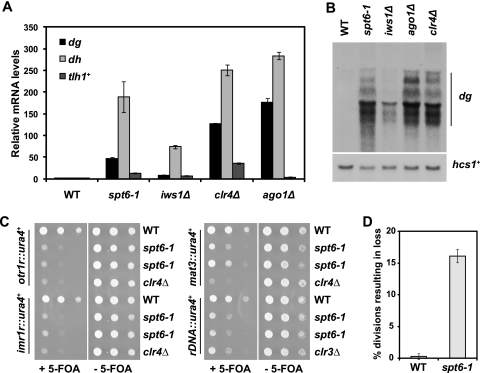
Fig. 2.
Spt6 is required for silencing of all heterochromatic loci. (A) Measurement of transcript levels of the pericentric dg and dh repeats and the subtelomeric gene tlh1+ by quantitative PCR in spt6-1 and iws1Δ mutants. The clr4Δ and ago1Δ mutants served as positive controls, and act1+ served as a control for normalization across samples. Each column represents the mean normalized value ± standard error (SE) (n = 3 to 6). (B) Northern analysis of transcript levels over the pericentric dg repeats, with hcs1+ serving as a loading control. The dg repeat is present in multiple copies in the genome and consequently produces several transcripts, ranging in size from ∼3.5 to ∼1.5 kb. (C) ura4+ silencing reporters inserted at the outer (otr1R) or inner (imr1R) centromeric repeats, the mating type locus (mat3), and rDNA loci (rDNA) were used to assess silencing in the spt6-1 mutant. Cells were serially diluted and spotted onto media with and without 5-FOA. Failure to grow on 5-FOA indicates defective silencing. The clr4Δ and clr3Δ strains served as positive controls for loss of silencing. The results shown are after incubation at 30°C for 3 days. (D) Genomic stability was assessed by monitoring inheritance of the circular minichromosome CM3112 in wild-type (WT) and spt6-1 strains. Each column represents the mean normalized value ± SE (n = 4).