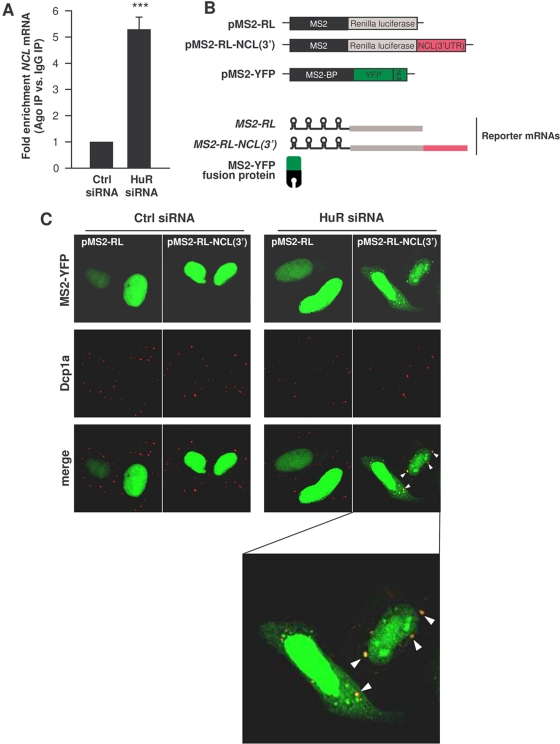
Fig. 5.
Silencing HuR increases the association of NCL mRNA with Ago and PBs. (A) By 48 h after transfection of either Ctrl siRNA or HuR siRNA, the interaction of NCL mRNA with Ago-containing complexes was assessed by RNP IP using anti-pan-Ago antibody followed by RT-qPCR analysis. (B) Schematic of the plasmids used for tracking the NCL mRNA intracellularly. pMS2-RL and pMS2-RL-NCL(3′) were derived from pSL-MS2(24X), and each expressed the Renilla luciferase (RL) coding region and 24 tandem MS2 RNA hairpins; pMS2-RL-NCL(3′) additionally contained the NCL 3′UTR. The plasmid pMS2-YFP expressed a fusion fluorescent protein (MS2-YFP) capable of binding MS2-containing RNA. NLS, nuclear localization signal. (C) Cells were transfected with either Ctrl or HuR siRNAs, together with pMS2-YFP and either pMS2-RL and pMS2-RL-NCL(3′). Forty-eight hours after transfection, the subcellular localization of the MS2-tagged RNAs was monitored by confocal microscopy. PBs were visualized by staining with an antibody that recognizes the PB marker Dcp1a. The “merge” panels show colocalization of MS2-tagged RNA and PBs. (The bottom panel shows an enlarged merged image in the HuR siRNA group to visualize colocalized [yellow] signals [arrowheads].)