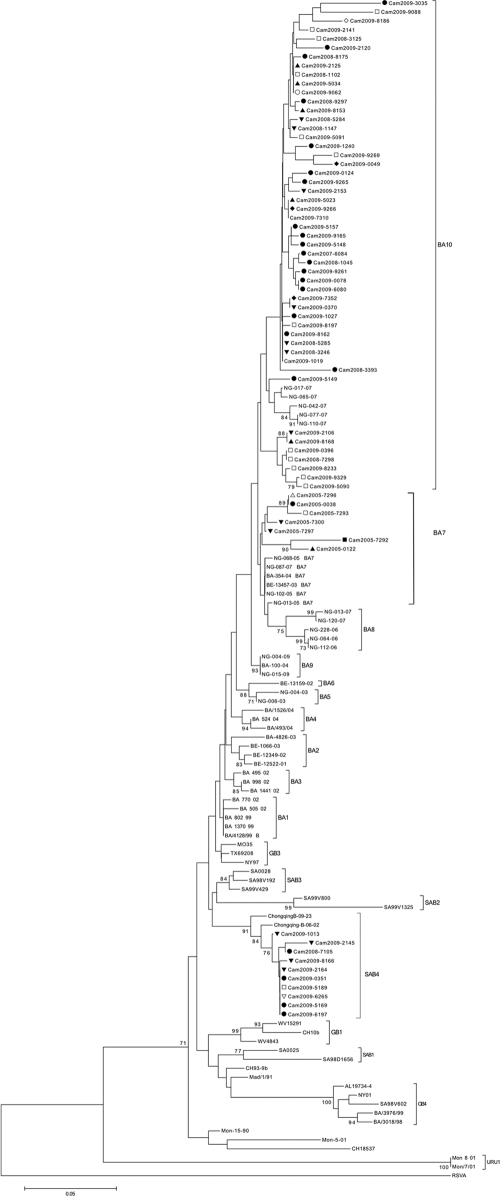
Fig. 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of the C-terminal second hypervariable region of the G gene of the Cambodian and reference HRSV group B isolates. An HRSV group A strain (GenBank accession number AF233900) was used as an outgroup. The prototype HRSV group B strain CH18537 (GenBank accession number M17213) and the prototype BA strain BA4128/99B (GenBank accession number AY333364) were also included. Phylogeny was constructed using the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Only bootstrap values of >70% are shown. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the p-distance method and were measured in the units of the number of base differences per site. Codon positions included were first, second, third, and noncoding. Cambodian strains are indicated by “Cam,” followed by the year of collection. Provinces in which samples were collected are indicated as follows: Koh Kong, ○; Prey Veng, *; Kampong Speu, ■; Kampong Cham, □; Kandal, ▵; Siem Reap, ▴; Phnom Penh, ▾; Takeo, ●; Sihanoukville, ▿; Battambang, ♦; Banteay Meanchey, ★; and Kampot, ♢. Following our phylogenetic analysis, we reclassified strains ChongqingB-09-23 and ChongqingB-06-02 as belonging to genotype SAB4.