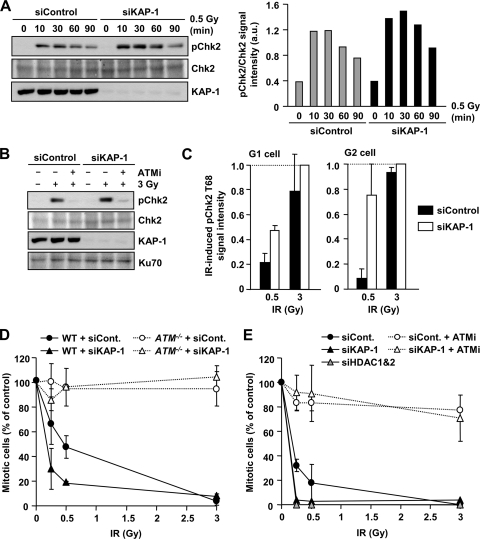
Fig. 3.
KAP-1 depletion enhances ATM signaling and G2/M checkpoint sensitivity. (A) Increased pChk2 is observed following KAP-1 depletion after IR. 1BR (WT) hTERT cells with or without KAP-1 siRNA were exposed to 0.5 Gy IR and harvested at the indicated time points. Quantification of the pChk2 bands normalized by total Chk2 is shown in right panel. Similar results were observed in two additional experiments. (B) IR-induced pChk2 is ATM dependent irrespective of KAP-1 status. 1BR (WT) hTERT cells with or without KAP-1 siRNA were exposed to 3 Gy of IR with or without 10 μM ATM inhibitor and harvested 2 h post-IR. (C) Enhanced pChk2 signal is observed in KAP-1 depleted cells by IF. 1BR (WT) hTERT cells with or without KAP-1 siRNA were fixed and stained with pChk2, CENPF, and DAPI 30 min after IR. The signal intensity was analyzed by using ImageJ. G2-phase cells were identified by CENP-F. Anti-pChk2 antibody specificity was confirmed as described previously (30). The results represent the mean ± the SD from two experiments. (D) KAP-1 siRNA knockdown causes hypersensitive G2/M checkpoint arrest. WT and ATM−/− MEFs were subjected to KAP-1 siRNA. After IR, cells were fixed 1 h later and stained with anti-p-H3 Ser10 and DAPI. The numbers of p-H3 Ser10+ cells were scored and normalized to the nonirradiated control. (E) KAP-1 and HDAC1/2 depletion increase the sensitivity of G2/M checkpoint arrest. A549 cells were subjected to KAP-1 siRNA with or without ATMi or HDAC1/2 double siRNA. The percent mitotic cells 2 h after IR were scored. The results represent the means and the SD from three experiments (D and E).