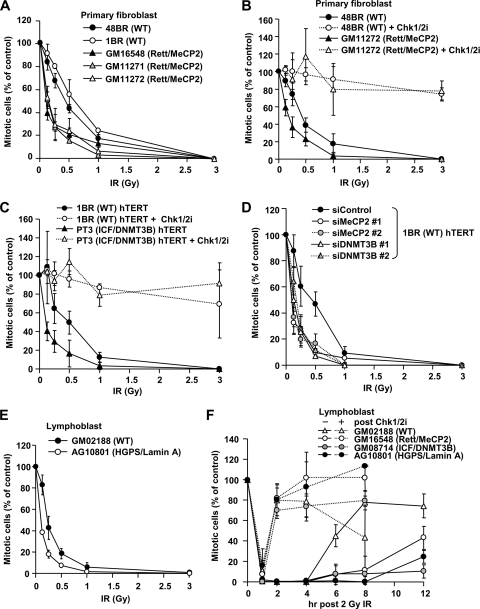
Fig. 7.
Cell lines from Rett, ICF, and HGPS patients show hypersensitive IR-induced G2/M checkpoint arrest. (A) Rett fibroblast cells exhibit hypersensitive G2/M checkpoint arrest after IR. Two control (48BR and 1BR) and three Rett syndrome (GM16548, GM11271, and GM11272) primary fibroblast lines were analyzed for G2/M checkpoint arrest. (B) Enhanced initiation of checkpoint sensitivity in Rett fibroblast cells is abolished by adding the Chk1/Chk2 inhibitor. The Chk1/Chk2 inhibitor, SB218078, was added 30 min prior to IR. (C) ICF fibroblast cells show hypersensitive G2/M checkpoint arrest. 1BR (WT) and PT3 (ICF/DNMT3) hTERT cells were analyzed for G2/M checkpoint arrest. The inhibitor was added 30 min prior to IR. (D) Depletion of MeCP2 and DNMT3B confers hypersensitive G2/M checkpoint arrest. 1BR (WT) hTERT cells were subjected to MeCP2 and DNMT3B siRNA. Two distinct siRNA oligonucleotides, 1 and 2, were used for each MeCP2 and DNMT3B knockdown. (E) HGPS patient (AG10801) LBLs show hypersensitive G2/M checkpoint arrest. (F) LBLs from patients with HC disorder exhibit prolonged G2/M checkpoint arrest after IR. The maintenance of G2/M checkpoint arrest was examined in control (GM02188), Rett (GM16548), ICF (GM08714), and HGPS (AG10801) LBLs. LBLs were used for this analysis to allow direct comparison between all patient lines, because efficiently growing HGPS cells were only available as LBLs. Consistent with fibroblast cell lines, Rett and ICF patient LBLs showed hypersensitive initial G2/M checkpoint arrest after low-dose IR (data not shown). Aphidicolin (APH) at 4 μM was added immediately after 2 Gy of IR. We have not examined 12-h time point in the inhibitor-treated cells because of cellular toxicity by the drug. The mitotic index was measured using p-H3 Ser10 at 1 h after irradiation (A to E). Error bars represent the SD from three independent experiments (A to F).