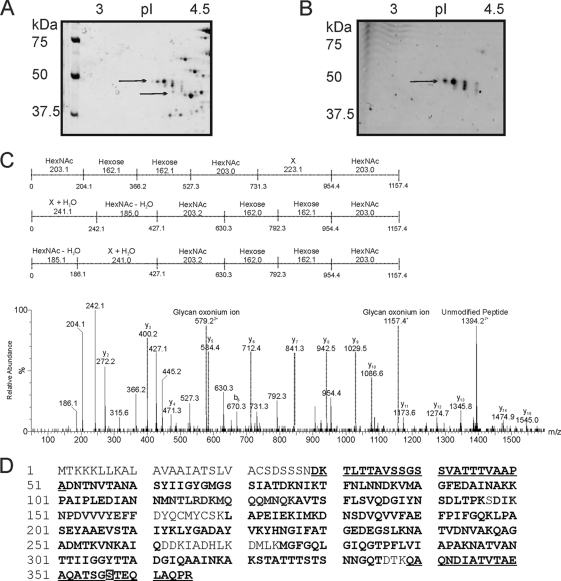
Fig. 1.
(A and B) Zoom images of DsbA protein from F. tularensis subsp. tularensis strain SchuS4 resolved by 2D gel and tandem mass spectrometry analysis of the putative glycopeptide. The pI gradient is shown at the top of the gels, and the positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown to the left of the gels. (A) F. tularensis subsp. tularensis strain SchuS4 stained with Sypro Ruby. Wild-type SchuS4 protein-stained image shows 4 protein spots that were identified by nLC-MSMS of their tryptic digests as DsbA. (B) F. tularensis subsp. tularensis strain SchuS4 stained with Emerald Q glycostain. The gel shows three predominant glycol-reactive protein spots, corresponding to DsbA. Proteins with different molecular masses and pIs in panels A and B are indicated by the black arrows. (C) nLC-MS/MS spectrum of the quadruply protonated T343–365 glycopeptide at m/z 986.7. In the spectrum shown at the bottom of the panel, relative abundance is shown on the y axis, and m/z is shown on the x axis. The spectrum is dominated in the high-m/z region by a doubly protonated ion corresponding to the unmodified peptide. Peptide related y and b type fragment ions are indicated. The glycopeptide was 1.156 Da heavier than the unmodified peptide. A glycan-related oxonium ion was visible at m/z 1,157. In addition, a series of ions that did not correspond to peptide ions were clearly visible. These ions were characterized by a series of neutral losses from m/z 1,157, comprising six losses at 203, 162, 162, 203, 223, and 203 (in the order shown) and the same monosaccharides in the reverse orientation, 203, 223, 203, 162, 162, and 203. These masses could plausibly represent monosaccharides such as HexNAc (203) and hexose (162). The loss of 223 does not correspond to a known monosaccharide and is indicated as X in the figure. (D) Peptide sequence coverage obtained from MS/MS sequencing of DsbA digested with either trypsin or Asp-N. Sequenced peptides are indicated in bold type, and glycopeptides are shown in bold type and underlined. A glycopeptide, at the N-terminal region of the protein was identified: 29DKTLTTAVSSGSSVATTTVAAPA51. Another glycopeptide, 343DIATVTAEAQATSGSTEQLAQPR367, the Asp-N fragment of tryptic digests, was detected in DsbA gel spots, and the mapped glycosylation site of the T32 glycopeptide is indicated in white-on-black type.