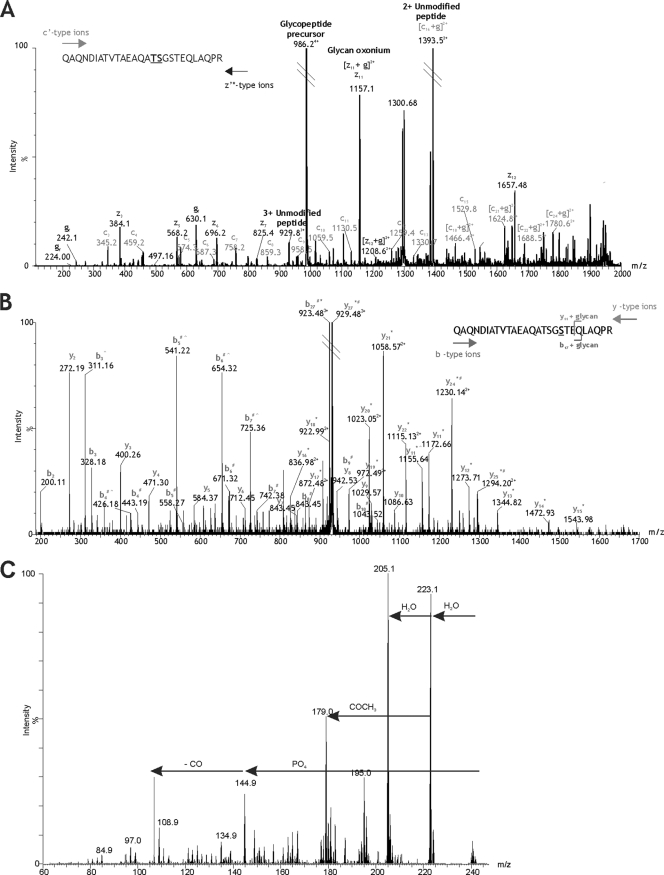
Fig. 2.
Mapping the modification site of DsbA T343–365 glycopeptide. (A) ETD mass spectrum of the IP-NPLC-purified glycopeptide precursor ion at m/z 986.604+. Peptide c′ and z′* type ions are annotated. A modified amino acid can be detected in an ETD spectrum by a peak corresponding to a c′ or z′* ion plus the glycan mass. The additional mass of the glycan is then observed for each of the subsequent c′ and z′* ions. The glycan (g)-modifying peptide T343–365 is 1,156.41 Da. A prominent peak at m/z 1,157.12 could represent [z11 + g]2+ (m/z 1,156.78), indicating that serine 355 is the site of modification. However, this peak could also represent the predicted m/z of z11 (m/z 1,157.56) and the glycan oxonium ion (m/z 1,157.41). Since the resolution is insufficient to assign charge state, serine 355 cannot be unambiguously annotated as the site of glycosylation. Threonine 354 also cannot be unambiguously annotated as the site of glycosylation, despite a prominent ion at m/z 1,394.52, which may represent [c16 + g]2+ (m/z 1,393.90) as well as the doubly charged unmodified peptide ion (m/z 1,393.68). The fact that these two amino acids are adjacent to one another further adds to the uncertainty because neither is able to provide additional evidence for modification of the residue next to it. In this case, ETD produces two candidate amino acid residues for the site of glycosylation: threonine 354 and serine 355. (B) nLC-MS/MS spectrum of the triply charged β-eliminated peptide ion at m/z 929.48 isolated by IP-NPLC separation. Peptide y and b type ions are indicated. Glycan removal by β-elimination with NH4OH results in loss of 1 Da from the modified amino acid residue. An observed loss of 1 Da (*) from the predicted y11 peptide ion to the N-terminal y27 peptide ion indicates that serine 355 is the site of glycosylation. Deamidation of the sole asparagine residue in the peptide sequence results in a 1-Da addition (#) to the b4 peptide ion, which is also observed for all subsequent b ions detected to the C-terminal b27 peptide ion. The loss of 1 Da due to β-elimination and the addition of 1 Da due to deamidation results in no net m/z difference between the predicted unmodified peptide precursor ion and the observed β-eliminated peptide precursor ion. The same is true for several peptide fragment ions at either end of the sequence that are subject to both β-elimination and deamidation. Additionally, a gas phase neutral loss of NH3 (∧) from the side chain of glutamine 341 results in several prominent peaks in the mid-m/z region corresponding to b ions 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 minus 17 Da. A gas phase neutral loss of 17 Da was also observed for the β-eliminated y11 peptide ion. (C) MS3 analysis of unknown monosaccharide m/z 242. From the MS/MS spectrum of the quadruply protonated T343–365 glycopeptide at m/z 986.7, the glycan monosaccharide-related ion at m/z 242.1 was selected for MS3 analysis. The resulting spectrum is shown, with plausible losses of functional groups indicated. Sequential losses of water and a putative phosphate group resulted in a mass of 144.1. MS4 analysis of the fragment ion m/z 144.9 yielded a single daughter ion at m/z 116.9 (possible loss of CO) (data not shown).