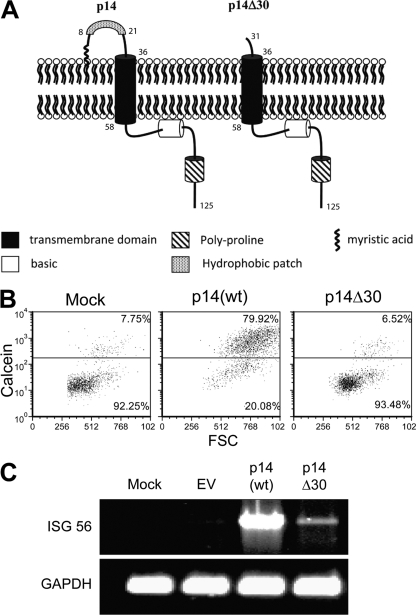
Fig. 1.
p14(wt), but not the ectodomain mutant p14Δ30, is capable of inducing pore formation and ISG 56 mRNA accumulation. (A) Schematic diagram of the important domains within the p14 proteins. The p14Δ30 mutant lacks the first 30 NH2-terminal amino acids, including the hydrophobic patch. (B) The extent of pore formation was measured by adding calcein red-labeled Vero cells to QM5 cells cotransfected with eGFP and p14(wt) or p14Δ30 for 4 h. Pore formation was quantified by analyzing the percentage of gated eGFP-expressing cells that acquired the calcein red from the Vero cells, plotted against the forward scatter (FSC). (C) Vero cells transfected with pcDNA3.1 (EV), p14(wt), or p14Δ30 plasmid DNA were washed, trypsinized, and placed onto naïve human embryonic lung fibroblasts. RNA was harvested at 16 h post-cell transfer, followed by RT-PCR using primers specific for human ISG56 and GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase).