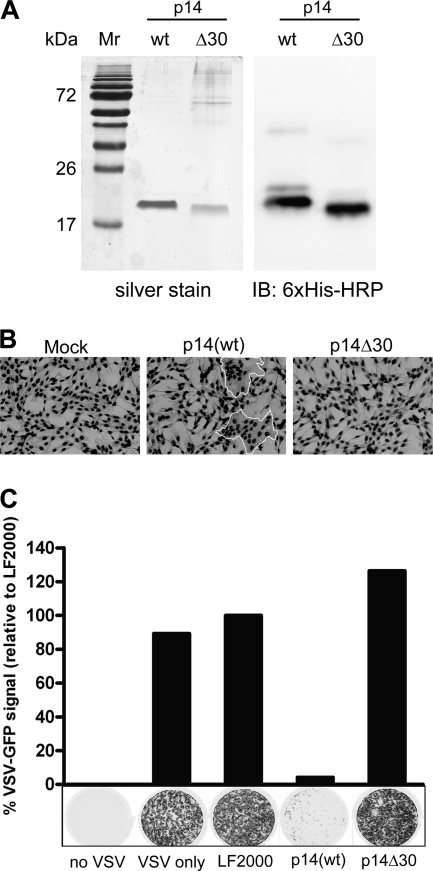
Fig. 2.
p14(wt)-Mediated cell-cell fusion induces an antiviral state in human fibroblasts. (A) Purification of p14 proteins following ion exchange chromatography. One microgram each of p14(wt) and p14Δ30 was run on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and silver stained. For Western immunoblot analysis, 100 ng each of p14(wt) and p14Δ30 was run on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane. A horseradish peroxidase-conjugated 6×His antibody was used to detect the p14 proteins. Mr, molecular mass marker. (B) QM5 cells were transfected with 4 μg of purified p14(wt) or p14Δ30 proteins for 8 h to allow fusion to proceed. Cells were fixed and Giemsa stained, and light microscopy images were captured at a magnification of ×200. Syncytia are outlined in white. (C) Following a 24-h treatment with purified p14(wt) or p14Δ30 proteins, human fibroblasts were infected with VSV expressing GFP from the viral promoter. GFP fluorescence was detected 24 h postinfection using a Typhoon Trio imager (GE Healthcare). Results from a representative experiment are presented. The level of GFP expression was quantified using ImageQuant TL software (GE Healthcare) and expressed as a percentage of fluorescence relative to that of LF2000-treated wells. Cells incubated with no VSV or VSV only were included as controls.