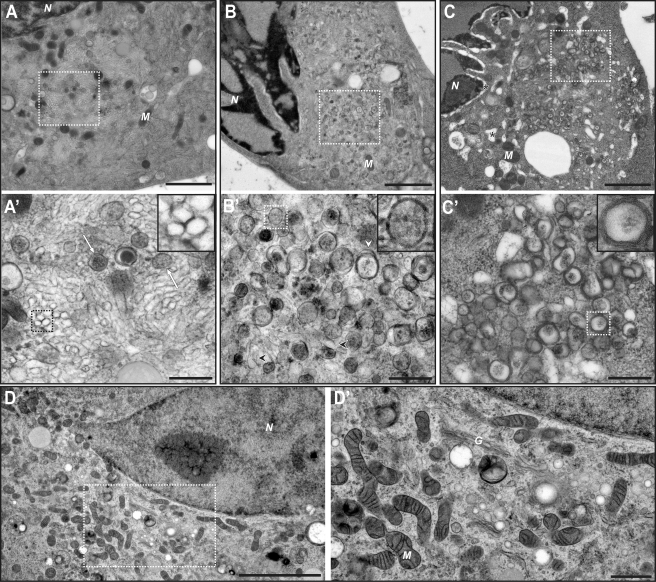
FIG 2 .
Electron micrographs of CVB3-infected Vero E6 cells, high-pressure frozen at 5 h p.i. (A and A′), 6 h p.i. (B and B′), and 7 h p.i. (C and C′). (A) At 5 h p.i., large clusters of virus-induced modifications are observed in the perinuclear region. (A′) The clusters consist predominantly of single-membrane elongated structures, which appear to be tubules sometimes visualized in cross section (inset). Some DMVs (white arrows) can also be detected. (B) As infection progresses (6 h p.i.), the perinuclear clusters change. (B′) Single-membrane structures (black arrowheads) are sparser, whereas DMVs (inset) become more common. Compartments surrounded by more than two membranes (white arrowhead) start to be frequently observed. (C) At 7 h p.i., severe cytopathic effects, such as dilation of the ER and nuclear envelope, become apparent (asterisks). (C′) At this stage, CVB3-induced modifications consist of DMVs and more complex multilamellar structures (inset). (D and D′) Micrographs of a mock-infected Vero E6 cell are shown for comparison. N, nucleus; M, mitochondrion, G, Golgi complex. Panels A′, B′, C′, and D′ show higher-resolution images of the boxed areas in panels A, B, C, and D, respectively. Scale bars, 2 µm (A, B, and C), 500 nm (A′, B′, and C′), 5 µm (D), and 1 µm (D′).