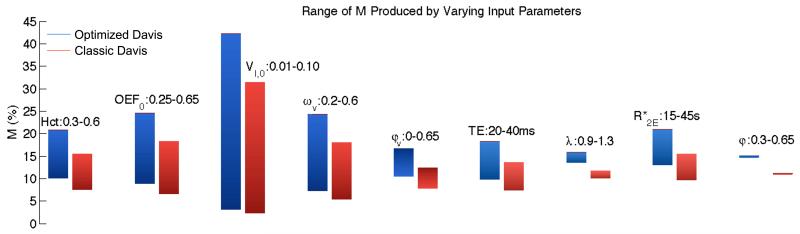
Figure 5. Range of M for classic and optimized Davis models as input parameters vary.
(The parameters are: Hct=hematocrit, OEF0=baseline O2 extraction fraction, VI,0=baseline CBV fraction, ωv=baseline venous CBV fraction, φv=exponent relating venous CBV changes to CBF, TE=echo time, λ=intravascular to extravascular spin density ratio, =intrinsic extravascular signal decay rate, and φ=exponent relating total CBV changes to CBF.) Values for M associated with the standard physiology for the two models are classic M=11.1 and optimized M=14.9. Note the gradient of the bars corresponds to the ranges of the input parameters; the lowest values of the inputs are associated with the dark end of the bars and the highest values are associated with the light end of the bars. Specifically note the large variation in M due to VI,0. Also as expected doubling TE approximately doubles calculated M. There is much smaller variation in M for φv, but sizeable variation in M due to Hct, OEF0, and ωv, consistent with the dependence of M on baseline deoxyhemoglobin-containing blood volume and deoxyhemoglobin concentration. Finally, the tissue relaxation rate constant, , also has a noticeable impact on M as expected.