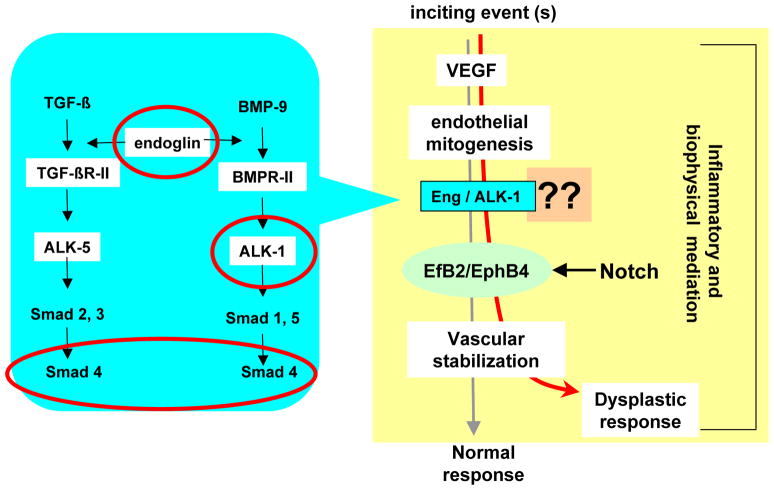
Fig. 1. Speculative synthesis of pathways involved in AVM pathogenesis.
The blue shaded area is a simplified summary of presumed ALK-1 and ENG signaling via TGF-β and BMP-9 in endothelial cells (EC); the genes mutated in HHT are circled. Main components of the scheme are (a) inciting event(s) upregulate the expression of angiogenic factors, such as VEGF, which induce EC mitogenesis; newly formed vessels will develop into a stable neovasculature; (b) this process leads to a vascular dysplastic response when signaling through aberrant ALK-1 and/or ENG, or in a closely related pathway (question marks); (c) ephrinB2 and EPHB4 imbalance, possibly through involvement of Notch signaling; and (d) modifier influences, potentially genetic and/or hemodynamic. Inflammation and involvement of circulating precursor cells may be relevant.